Energy balance-related factors and risk of colorectal cancer based on KRAS, PIK3CA, and BRAF mutations and MMR status
- PMID: 35546360
- PMCID: PMC9470639
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04019-9
Energy balance-related factors and risk of colorectal cancer based on KRAS, PIK3CA, and BRAF mutations and MMR status
Abstract
Introduction: KRAS mutations (KRASmut), PIK3CAmut, BRAFmut, and mismatch repair deficiency (dMMR) have been associated with the Warburg-effect. We previously observed differential associations between energy balance-related factors (BMI, clothing-size, physical activity) and colorectal cancer (CRC) subtypes based on the Warburg-effect. We now investigated whether associations between energy balance-related factors and risk of CRC differ between subgroups based on mutation and MMR status.
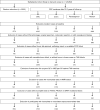
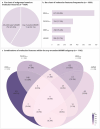
Methods: Information on molecular features was available for 2349 incident CRC cases within the Netherlands Cohort Study (NLCS), with complete covariate data available for 1934 cases and 3911 subcohort members. Multivariable-adjusted Cox-regression was used to estimate associations of energy balance-related factors with risk of CRC based on individual molecular features (KRASmut; PIK3CAmut; BRAFmut; dMMR) and combinations thereof (all-wild-type + MMR-proficient (pMMR); any-mutation/dMMR).
Results: In men, BMI and clothing-size were positively associated with risk of colon, but not rectal cancer, regardless of molecular features subgroups; the strongest associations were observed for PIK3CAmut colon cancer. In women, however, BMI and clothing-size were only associated with risk of KRASmut colon cancer (p-heterogeneityKRASmut versus all-wild-type+pMMR = 0.008). Inverse associations of non-occupational physical activity with risk of colon cancer were strongest for any-mutation/dMMR tumors in men and women, and specifically for PIK3CAmut tumors in women. Occupational physical activity was inversely associated with both combination subgroups of colon cancer in men.
Conclusion: In men, associations did not vary according to molecular features. In women, a role of KRAS mutations in the etiological pathway between adiposity and colon cancer is suggested, and of PIK3CA mutations between physical activity and colon cancer.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Energy balance; Etiological heterogeneity; Mismatch repair/microsatellite instability; Mutations; Prospective cohort study.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
H. I. Grabsch: Honorarium from Astra Zeneca and BMS for scientific advisory board activities not related to the current study.
Figures
References
-
- Campbell PT, Jacobs ET, Ulrich CM, Figueiredo JC, Poynter JN, McLaughlin JR, Haile RW, Jacobs EJ, Newcomb PA, Potter JD (2010) Case–control study of overweight, obesity, and colorectal cancer risk, overall and by tumor microsatellite instability status. J Natl Cancer Inst 102(6):391–400 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carr P, Alwers E, Bienert S, Weberpals J, Kloor M, Brenner H, Hoffmeister M (2018) Lifestyle factors and risk of sporadic colorectal cancer by microsatellite instability status: a systematic review and meta-analyses. Ann Oncol 29(4):825–834 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

