Indole alkaloids as potential candidates against COVID-19: an in silico study
- PMID: 35546368
- PMCID: PMC9094126
- DOI: 10.1007/s00894-022-05137-4
Indole alkaloids as potential candidates against COVID-19: an in silico study
Abstract
COVID-19 has recently grown to be pandemic all around the world. Therefore, efforts to find effective drugs for the treatment of COVID-19 are needed to improve humans' life quality and survival. Since the main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2 plays a crucial role in viral replication and transcription, the inhibition of this enzyme could be a promising and challenging therapeutic target to fight COVID-19. The present study aims to identify alkaloid compounds as new potential inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 Mpro by the hybrid modeling analyses. The docking-based virtual screening method assessed a collection of alkaloids extracted from over 500 medicinal plants and sponges. In order to validate the docking process, classical molecular dynamic simulations were applied on selected ligands, and the calculation of binding free energy was performed. Based on the proper interactions with the active site of the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, low binding energy, few side effects, and the availability in the medicinal market, two indole alkaloids were found to be potential lead compounds that may serve as therapeutic options to treat COVID-19. This study paves the way for developing natural alkaloids as stronger potent antiviral agents against the SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Docking; Indole alkaloids; MM-PBSA; Molecular dynamic simulations; SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitor; Virtual screening.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





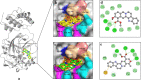
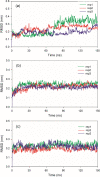
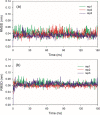

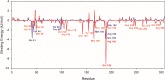
References
-
- Sharifkashani S, Bafrani MA, Khaboushan AS, Pirzadeh M, Kheirandish A, Yavarpour Bali H, Hessami A, Saghazadeh A, Rezaei N. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and SARS-CoV-2: potential therapeutic targeting. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;884:173455. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173455. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gupta SP (2017) Viral proteases and their inhibitors. 1st Edition, Academic Press.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

