Biological Effects of Aqueous Extract of Laurus noboilis L. Leaves on Some Histological and Immunological Parameters in Male Rat Liver Affected by Aluminum Chloride
- PMID: 35546977
- PMCID: PMC9083872
- DOI: 10.22092/ari.2021.356361.1827
Biological Effects of Aqueous Extract of Laurus noboilis L. Leaves on Some Histological and Immunological Parameters in Male Rat Liver Affected by Aluminum Chloride
Abstract
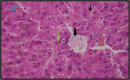
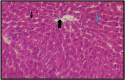
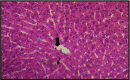
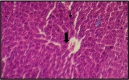
The present current study aimed to assess the protective effect of the aqueous extract of Laurus noboilis L. leaves against the toxic effects of aluminum chloride on liver tissue. A number of 36 male albino rats (Wistar) were randomly assigned to six groups (n=6) and treated for 30 days: Group 1 was regarded as the control group, Group 2 received Aluminum Chloride 90 mg/kg body weight orally by gavage, Group3: normal rats received aqueous extracts of Lurus Nobilis L. leaf 150 mg/kg body weight, Group 4: normal rats received aqueous extracts of Lurus Nobilis L. leaf 200 mg/kg body weight, Group 5: normal rats received aqueous extracts of Lurus Nobilis L. leaf 150 mg/kg body weight after a period of 4 h following treatment by Aluminum Chloride 90 mg/kg body weight, Group 6: normal rats received aqueous extracts of Laurus nobilis L. 200 mg /kg after a period of 4 h following treatment by Aluminum chloride with 90 mg/kg body weight. All the experimental animals were sacrificed, and sections of their liver were stained with Hematoxylin-Eosin for histological evaluations. Moreover, the liver enzymes and immune cytokines, such as Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), and interleukin-10 (IL-10) were measured. As evidenced by the results of the current study, treatment with aqueous extract of Lurus Nobilis L. leaves at a dose of 150 and 200 mg/kg body weight orally contributed to the mitigation of the toxic effects of Aluminum Chloride in albino rats by reducing the damage and inflammation in the hepatocytes. The study suggested that the aqueous extract of Lurus Nobilis L. enhances the protective effect against liver toxicity.
Keywords: Aluminum chloride; Cytokines; Hepatocyte; Interleukin-10; Lurus Nobilis.
Figures


References
-
- AL-Samarrai OR, Naji NA, Hameed RR. Effect of Bay leaf (Laurus nobilis L.) and its isolated (flavonoids and glycosides) on the lipids profile in the local Iraqi female rabbits. Tikrit J Pure Sci. 2018;22(6):72–5.
-
- Parthasarathy VA, Chempakam B, Zachariah TJ. Chemistry of spices. Cabi: 2008.
-
- Sharma M, Sharma R. Coriander. Handbook of herbs and spices. Elsevier: 2012. pp. 216–49.
-
- Dias MI, Barros L, Dueñas M, Alves RC, Oliveira MBP, Santos-Buelga C, et al. Nutritional and antioxidant contributions of Laurus nobilis L. leaves: would be more suitable a wild or a cultivated sample? Food Chem. 2014;156:339–46. - PubMed
-
- Orchard A, Sandasi M, Kamatou G, Viljoen A, van Vuuren S. The in vitro antimicrobial activity and chemometric modelling of 59 commercial essential oils against pathogens of dermatological relevance. Chem Biodivers. 2017;14(1):1600218. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
