Non-homologous End Joining-Mediated Insertional Mutagenesis Reveals a Novel Target for Enhancing Fatty Alcohols Production in Yarrowia lipolytica
- PMID: 35547152
- PMCID: PMC9082995
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.898884
Non-homologous End Joining-Mediated Insertional Mutagenesis Reveals a Novel Target for Enhancing Fatty Alcohols Production in Yarrowia lipolytica
Abstract
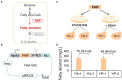
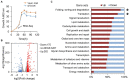
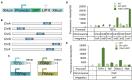
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)-mediated integration is effective in generating random mutagenesis to identify beneficial gene targets in the whole genome, which can significantly promote the performance of the strains. Here, a novel target leading to higher protein synthesis was identified by NHEJ-mediated integration that seriously improved fatty alcohols biosynthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica. One batch of strains transformed with fatty acyl-CoA reductase gene (FAR) showed significant differences (up to 70.53-fold) in fatty alcohol production. Whole-genome sequencing of the high-yield strain demonstrated that a new target YALI0_A00913g ("A1 gene") was disrupted by NHEJ-mediated integration of partial carrier DNA, and reverse engineering of the A1 gene disruption (YlΔA1-FAR) recovered the fatty alcohol overproduction phenotype. Transcriptome analysis of YlΔA1-FAR strain revealed A1 disruption led to strengthened protein synthesis process that was confirmed by sfGFP gene expression, which may account for enhanced cell viability and improved biosynthesis of fatty alcohols. This study identified a novel target that facilitated synthesis capacity and provided new insights into unlocking biosynthetic potential for future genetic engineering in Y. lipolytica.
Keywords: RNA-Seq; Yarrowia lipolytica; fatty alcohols; new target identification; non-homologous end joining-mediated integration.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zhang, Bai, Fang, Song and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

