Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica to Produce Itaconic Acid From Waste Cooking Oil
- PMID: 35547171
- PMCID: PMC9083544
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.888869
Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica to Produce Itaconic Acid From Waste Cooking Oil
Abstract
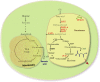
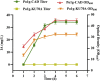
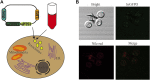
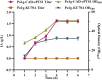
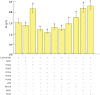
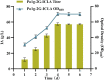
Itaconic acid (IA) is a high-value organic acid with a plethora of industrial applications. In this study, we seek to develop a microbial cell factory that could utilize waste cooking oil (WCO) as raw material for circular and cost-effective production of the abovementioned biochemical. Specifically, we expressed cis-aconitic acid decarboxylase (CAD) gene from Aspergillus terreus in either the cytosol or peroxisome of Yarrowia lipolytica and assayed for production of IA on WCO. To further improve production yield, the 10 genes involved in the production pathway of acetyl-CoA, an intermediate metabolite necessary for the synthesis of cis-aconitic acid, were individually overexpressed and investigated for their impact on IA production. To minimize off-target flux channeling, we had also knocked out genes related to competing pathways in the peroxisome. Impressively, IA titer up to 54.55 g/L was achieved in our engineered Y. lipolytica in a 5 L bioreactor using WCO as the sole carbon source.
Keywords: Y. lipolytica; itaconic acid; peroxisome; subcellular engineering; waste cooking oil.
Copyright © 2022 Rong, Miao, Wang, Wang, Liu, Lu, Zhao, Zhang, Xiao, Pushpanathan, Wong and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Engineering the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica to produce limonene from waste cooking oil.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019 Oct 8;12:241. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1580-y. eCollection 2019. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019. PMID: 31624503 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced itaconic acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica via heterologous expression of a mitochondrial transporter MTT.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Mar;103(5):2181-2192. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09627-z. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30656392
-
High-yield α-humulene production in Yarrowia lipolytica from waste cooking oil based on transcriptome analysis and metabolic engineering.Microb Cell Fact. 2022 Dec 24;21(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01986-z. Microb Cell Fact. 2022. PMID: 36566177 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial itaconic acid bioproduction towards sustainable development: Insights, challenges, and prospects.Bioresour Technol. 2023 Sep;384:129280. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129280. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Bioresour Technol. 2023. PMID: 37290713 Review.
-
Biotechnological production of itaconic acid and its biosynthesis in Aspergillus terreus.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009 Sep;84(4):597-606. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2132-3. Epub 2009 Jul 21. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19629471 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Engineering of Filamentous Fungus Trichoderma reesei for Itaconic Acid Production.J Agric Food Chem. 2025 Feb 26;73(8):4716-4724. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c10107. Epub 2025 Feb 18. J Agric Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39963051
-
Enhanced production of amyrin in Yarrowia lipolytica using a combinatorial protein and metabolic engineering approach.Microb Cell Fact. 2022 Sep 9;21(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01915-0. Microb Cell Fact. 2022. PMID: 36085205 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered microbial consortia for next-generation feedstocks.Biotechnol Notes. 2024 Jan 17;5:23-26. doi: 10.1016/j.biotno.2024.01.002. eCollection 2024. Biotechnol Notes. 2024. PMID: 39416694 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Genomic and Phenotypic Landscape of the Oleaginous Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jan 4;9(1):76. doi: 10.3390/jof9010076. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36675897 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effective production of squalene using Yarrowia lipolytica via metabolic engineering and fermentation engineering.Biotechnol Lett. 2025 May 5;47(3):49. doi: 10.1007/s10529-025-03591-7. Biotechnol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40323463
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

