Evaluating a Panel of Autoantibodies Against Tumor-Associated Antigens in Human Osteosarcoma
- PMID: 35547257
- PMCID: PMC9081566
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.872253
Evaluating a Panel of Autoantibodies Against Tumor-Associated Antigens in Human Osteosarcoma
Abstract
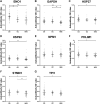
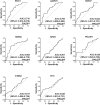
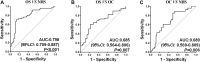
Background: The aim of this study was to identify a panel of candidate autoantibodies against tumor-associated antigens in the detection of osteosarcoma (OS) so as to provide a theoretical basis for constructing a non-invasive serological diagnosis method in early immunodiagnosis of OS. Methods: The serological proteome analysis (SERPA) approach was used to select candidate anti-TAA autoantibodies. Then, indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to verify the expression levels of eight candidate autoantibodies in the serum of 51 OS cases, 28 osteochondroma (OC), and 51 normal human sera (NHS). The rank-sum test was used to compare the content of eight autoantibodies in the sera of three groups. The diagnostic value of each indicator for OS was analyzed by an ROC curve. Differential autoantibodies between OS and NHS were screened. Then, a binary logistic regression model was used to establish a prediction logistical regression model. Results: Through ELISA, the expression levels of seven autoantibodies (ENO1, GAPDH, HSP27, HSP60, PDLIM1, STMN1, and TPI1) in OS patients were identified higher than those in healthy patients (p < 0.05). By establishing a binary logistic regression predictive model, the optimal panel including three anti-TAAs (ENO1, GAPDH, and TPI1) autoantibodies was screened out. The sensitivity, specificity, Youden index, accuracy, and AUC of diagnosis of OS were 70.59%, 86.27%, 0.5686, 78.43%, and 0.798, respectively. Conclusion: The results proved that through establishing a predictive model, an optimal panel of autoantibodies could help detect OS from OC or NHS at an early stage, which could be used as a promising and powerful tool in clinical practice.
Keywords: autoantibody; detection; early diagnosis; osteosarcoma; panel; tumor-associated antigen.
Copyright © 2022 Luo, Wu, Ma, Liang, Luo, Gu, Fan, Hao, Li and Xing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunoseroproteomic profiling in autoantibody to ENO1 as potential biomarker in immunodiagnosis of osteosarcoma by serological proteome analysis (SERPA) approach.Oncoimmunology. 2021 Sep 24;10(1):1966969. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1966969. eCollection 2021. Oncoimmunology. 2021. PMID: 38260036 Free PMC article.
-
Using a panel of multiple tumor-associated antigens to enhance the autoantibody detection in the immunodiagnosis of ovarian cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Mar;120(3):3091-3100. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27497. Epub 2018 Nov 28. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30484895
-
Using protein microarray to identify and evaluate autoantibodies to tumor-associated antigens in ovarian cancer.Cancer Sci. 2021 Feb;112(2):537-549. doi: 10.1111/cas.14732. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33185955 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-Associated Antigens (TAAs) for the Serological Diagnosis of Osteosarcoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 30;12:665106. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.665106. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying autoantibody signatures in cancer: a promising challenge.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2009 Aug;6(4):377-86. doi: 10.1586/epr.09.56. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19681673 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of ENO1 and its targeted therapy in tumors.J Transl Med. 2024 Nov 14;22(1):1025. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05847-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39543641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Expression of ENO1 and Low Levels of Circulating Anti-ENO1 Autoantibodies in Patients with Myelodysplastic Neoplasms and Acute Myeloid Leukaemia.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 22;16(5):884. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050884. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen S.-S., Li K., Wu J., Peng Z.-Y., Wang Z.-D., Wang J.-C., et al. (2020). Stem Signatures Associated Antibodies Yield Early Diagnosis and Precise Prognosis Predication of Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 147, 223–233. 10.1007/s00432-020-03325-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

