Cromoglycate mesogen forms isodesmic assemblies promoted by peptides and induces aggregation of a range of proteins
- PMID: 35547307
- PMCID: PMC9085300
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra05226c
Cromoglycate mesogen forms isodesmic assemblies promoted by peptides and induces aggregation of a range of proteins
Abstract
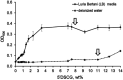
Disodium cromoglycate (5'DSCG) belongs to a class of nonamphiphilic molecules that form nematic chromonic liquid crystals in aqueous solutions. As the concentration increases, it is believed that the molecules first form isodesmic assemblies in water, which further align to form liquid crystal phases. However, the reports on isodesmic assemblies of 5'DSCG have been scarce. Herein, we show that the presence of peptides can promote the isodesmic assembly of 5'DSCG over a broad range of concentrations before reaching the liquid crystal phase. The presence of peptides can lower the 5'DSCG concentration in the aqueous solution to ∼1.5 wt% (from 11-12 wt%, forming a nematic liquid crystal phase) for isodesmic assembly formation. This result indicates a demixing between 5'DSCG and peptides in aqueous solution. We further explored this demixing mechanism to precipitate a wide range of proteins, namely, lectin A, esterase, lipase, bovine serum albumin, trypsin, and a pilin protein from bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. We found that 5'DSCG caused the aggregation of all these proteins except trypsin. These results, along with past findings, suggest that 5'DSCG isodesmic assemblies have the potential to assist in protein purification and crystallization.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Noncovalent polymerization and assembly in water promoted by thermodynamic incompatibility.J Phys Chem B. 2010 Aug 19;114(32):10357-67. doi: 10.1021/jp103143x. J Phys Chem B. 2010. PMID: 20701370
-
Stereochemical control of nonamphiphilic lyotropic liquid crystals: chiral nematic phase of assemblies separated by six nanometers of aqueous solvents.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Jun 13;117(23):7133-43. doi: 10.1021/jp401382h. Epub 2013 Jun 4. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23688325
-
The ability of single-chain surfactants to emulsify an aqueous-based liquid crystal oscillates with odd-even parity of alkyl-chain length.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2013 Dec 15;412:95-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2013.08.044. Epub 2013 Sep 11. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2013. PMID: 24144379
-
Nonamphiphilic assembly in water: polymorphic nature, thread structure, and thermodynamic incompatibility.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Jun 3;131(21):7430-43. doi: 10.1021/ja9015149. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19422237
-
Properties of the liquid crystals of some biopolymers.Adv Biophys. 1988;24:1-56. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(88)90003-2. Adv Biophys. 1988. PMID: 3077236 Review.
References
-
- Lydon J. Liq. Cryst. 2011;38:1663–1681. doi: 10.1080/02678292.2011.614720. - DOI
-
- Genkin M. M. Sokolov A. Lavrentovich O. D. Aranson I. S. Phys. Rev. X. 2017;7:011029.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

