Registration of Proximal Tibial Centre May Need to be Selectively Lateralized to Avoid Coronal Malalignment in Digitally-Assisted Knee Arthroplasty
- PMID: 35547340
- PMCID: PMC9043048
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-022-00601-y
Registration of Proximal Tibial Centre May Need to be Selectively Lateralized to Avoid Coronal Malalignment in Digitally-Assisted Knee Arthroplasty
Abstract
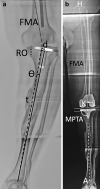
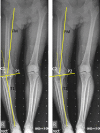
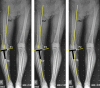
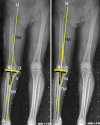
Purpose: Placement of prosthetic components and limb alignment can be adversely impacted by errors in identification of registration points in digitally assisted knee arthroplasty. The purpose of this study was to trigonometrically analyze the impact on the accuracy of coronal tibial component and limb alignment of discrepancy between the registered midpoint of the proximal bony tibia vis-à-vis the radiographic medio-lateral center of the lateralized final tibial implant in certain varus-deformed knees.
Methods: We analyzed trigonometrically the angular difference in coronal alignment of tibial component and hip-knee-ankle angle resulting from lateral translation of the medio-lateral center of the final tibial implant, with respect to the initial registered midpoint of the proximal bony tibia. was calculated using the equation tan( ) = d/t, where d is the numerical distance between the registered point and the center of the final tibial tray position and t is the length of tibia distal to the resection.
Results: One degree of varus malpositioning of the tibial component and the limb can occur for every 6.3 mm of lateral translation of the tibial implant with respect to the midpoint of the proximal bony tibia of average reported length (372 mm). The magnitude of this error is inversely proportional to tibial length and the patient's height.
Conclusions: Coronal malalignment of the tibial component and the limb is directly proportional to the amount of lateral translation of the tibial tray with respect to the registered midpoint of the proximal bony tibia and inversely proportional to the patient's height. This may occur in cases with tibial extra-articular deformity, those undergoing reduction osteotomy, downsizing of the tray, or inadvertently during tibial preparation. The error can be avoided by initial registration of the tibial midpoint more laterally by templating, re-registering the new center of the resected tibial surface or osteotomy for extra-articular deformity.
Keywords: Computer-assisted knee arthroplasty; Malalignment; Robotic knee arthroplasty; Total knee arthroplasty.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe author has no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Value of personalized extramedullary positioning technique on tibia side for coronal alignment of tibial prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Feb 15;36(2):177-182. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202108105. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35172402 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Seven phenotypes of varus osteoarthritic knees can be identified in the coronal plane.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Aug;30(8):2793-2805. doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06676-8. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. PMID: 34286347
-
[Evaluation and analysis of the tibial coronal alignment after total knee replacement with the extramedullary tibial cutting guided by the tibial tubercle and anterior tibial tendon in Chinese patients].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Apr 18;48(2):351-5. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 27080295 Chinese.
-
Intra- and Extra-Articular Deformity of Lower Limb: Tibial Condylar Valgus Osteotomy (TCVO) and Distal Tibial Oblique Osteotomy (DTOO) for Reconstruction of Joint Congruency.Adv Orthop. 2019 Feb 18;2019:8605674. doi: 10.1155/2019/8605674. eCollection 2019. Adv Orthop. 2019. PMID: 30906598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Component placement accuracy in two generations of handheld robotics-assisted knee arthroplasty.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021 Dec;141(12):2059-2067. doi: 10.1007/s00402-021-04040-6. Epub 2021 Jul 25. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021. PMID: 34304279 Review.
References
-
- Attada P, Ravindranadh G, Kumari K. Anthropometric measurement of maximum tibia length in south Indian population. Anatomical Sciences. 2018;15:57–64.
-
- Chavan SK, Chavan KD, Mumbre SS, Makhani CS. Stature and percutaneus tibial length: A correlational study in Maharashtrian population. Journal of Indian Academy of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. 2009;2(3):334–337.
-
- Dima D, Huang P, Suryanarayan P, Rosen A, Dima DD. Tibial tray rotation and posterior slope increase risk for outliers in coronal alignment: A virtual modelling investigation. Bone Joint Journal. 2020;102:43–48. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
