Small Things Matter: The 11.6-kDa TraB Protein is Crucial for Antibiotic Resistance Transfer Among Enterococci
- PMID: 35547396
- PMCID: PMC9083827
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.867136
Small Things Matter: The 11.6-kDa TraB Protein is Crucial for Antibiotic Resistance Transfer Among Enterococci
Abstract
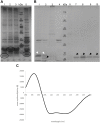
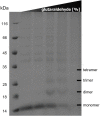
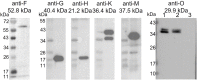
Conjugative transfer is the most important means for spreading antibiotic resistance genes. It is used by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, and archaea as well. Conjugative transfer is mediated by molecular membrane-spanning nanomachines, so called Type 4 Secretion Systems (T4SS). The T4SS of the broad-host-range inc18-plasmid pIP501 is organized in a single operon encoding 15 putative transfer proteins. pIP501 was originally isolated from a clinical Streptococcus agalactiae strain but is mainly found in Enterococci. In this study, we demonstrate that the small transmembrane protein TraB is essential for pIP501 transfer. Complementation of a markerless pIP501∆traB knockout by traB lacking its secretion signal sequence did not fully restore conjugative transfer. Pull-downs with Strep-tagged TraB demonstrated interactions of TraB with the putative mating pair formation proteins, TraF, TraH, TraK, TraM, and with the lytic transglycosylase TraG. As TraB is the only putative mating pair formation complex protein containing a secretion signal sequence, we speculate on its role as T4SS recruitment factor. Moreover, structural features of TraB and TraB orthologs are presented, making an essential role of TraB-like proteins in antibiotic resistance transfer among Firmicutes likely.
Keywords: Enterococcus; antibiotic resistance; conjugative transfer; plasmid; secretion complex; type IV secretion system.
Copyright © 2022 Berger, Michaelis, Probst, Sagmeister, Petrowitsch, Puchner, Pavkov-Keller, Gesslbauer, Grohmann and Keller.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


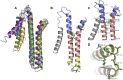
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

