Chronic Elevation of Skeletal Muscle [Ca2+]i Impairs Glucose Uptake. An in Vivo and in Vitro Study
- PMID: 35547584
- PMCID: PMC9083325
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.872624
Chronic Elevation of Skeletal Muscle [Ca2+]i Impairs Glucose Uptake. An in Vivo and in Vitro Study
Abstract
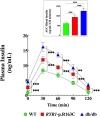
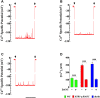
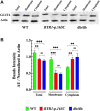
Skeletal muscle is the primary site of insulin-mediated glucose uptake through the body and, therefore, an essential contributor to glucose homeostasis maintenance. We have recently provided evidence that chronic elevated intracellular Ca2+ concentration at rest [(Ca2+)i] compromises glucose homeostasis in malignant hyperthermia muscle cells. To further investigate how chronic elevated muscle [Ca2+]i modifies insulin-mediated glucose homeostasis, we measured [Ca2+]i and glucose uptake in vivo and in vitro in intact polarized muscle cells from glucose-intolerant RYR1-p.R163C and db/db mice. Glucose-intolerant RYR1-p.R163C and db/db mice have significantly elevated muscle [Ca2+]i and reduced muscle glucose uptake compared to WT muscle cells. Dantrolene treatment (1.5 mg/kg IP injection for 2 weeks) caused a significant reduction in fasting blood glucose levels and muscle [Ca2+]i and increased muscle glucose uptake compared to untreated RYR1-p.R163C and db/db mice. Furthermore, RYR1-p.R163C and db/db mice had abnormal basal insulin levels and response to glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. In vitro experiments conducted on single muscle fibers, dantrolene improved insulin-mediated glucose uptake in RYR1-p.R163C and db/db muscle fibers without affecting WT muscle fibers. In muscle cells with chronic elevated [Ca2+]i, GLUT4 expression was significantly lower, and the subcellular fraction (plasma membrane/cytoplasmic) was abnormal compared to WT. The results of this study suggest that i) Chronic elevated muscle [Ca2+]i decreases insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and consequently causes hyperglycemia; ii) Reduced muscle [Ca2+]i by dantrolene improves muscle glucose uptake and subsequent hyperglycemia; iii) The mechanism by which chronic high levels of [Ca2+]i interfere with insulin action appears to involve the expression of GLUT4 and its subcellular fractionation.
Keywords: GLUT4; calcium; dantrolene; diabetes; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2022 Uryash, Mijares, Lopez, Adams and Lopez.
Conflict of interest statement
Author CL was employed by Wellmax Medical Center. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

