Fibrinogen-Albumin Ratio Index Exhibits Predictive Value of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Osteosarcoma
- PMID: 35547600
- PMCID: PMC9084387
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S358310
Fibrinogen-Albumin Ratio Index Exhibits Predictive Value of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Osteosarcoma
Abstract
Purpose: Inflammatory response and nutritional status are associated with cancer development and progression. The present study aimed to evaluate the predictive ability of the fibrinogen-albumin ratio index (FARI) to the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for osteosarcoma.
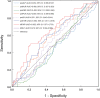
Patients and methods: A retrospective analysis involving 752 consecutive osteosarcoma patients between 2012 and 2020 was performed. Data on serum fibrinogen, albumin levels, white blood cell count, platelet count, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) before and after NAC were collected. The predictive value of the NAC efficacy in osteosarcoma was assessed by constructing a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and calculating the area under the curve (AUC). Prognosis and its predictive factors were analyzed by Kaplan-Meier method and COX regression analysis. Nomogram was established according to selected variables. The predictive performance of the nomogram model was assessed using C-statistics.
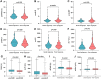
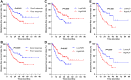
Results: A total of 203 patients were included. ROC analysis showed that both FARI before NAC (preFARI; AUC = 0.594, p = 0.032) and the change in FARI before and after NAC (dfFARI = preFARI-postFARI; AUC = 0.652, p = 0.001) exhibited more favorable predictive ability than ALP and other inflammation markers. The preFARI was divided into the high group (>6.1%) and the low group (≤6.1%) based on the optimal cut-off value of 6.1%. Patients with a high preFARI showed significantly decreased metastasis-free survival (MFS) and disease-free survival (DFS) (all p<0.01). In multivariable analysis, preFARI was an independent prognostic marker for patients with osteosarcoma. Predictive nomograms exhibited good ability to predict MFS (C-index = 0.748, se = 0.028) and DFS (C-index=0.727, se = 0.030).
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that FARI exhibits the favorable predictive ability for the efficacy of NAC for osteosarcoma, which could support clinicians and patients in clinical decision-making and treatment optimization.
Keywords: albumin; fibrinogen; fibrinogen–albumin ratio index; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; osteosarcoma; prognosis.
© 2022 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Harrison DJ, Geller DS, Gill JD, Lewis VO, Gorlick R. Current and future therapeutic approaches for osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2018;18:39–50. - PubMed
-
- Ritter J, Bielack SS. Osteosarcoma. Ann Oncol. 2010;21(Suppl 7):vii320–325. - PubMed
-
- Stiller CA, Bielack SS, Jundt G, Steliarova-Foucher E. Bone tumours in European children and adolescents, 1978-1997. Report from the Automated Childhood Cancer Information System project. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:2124–2135. - PubMed
-
- Ji S-Y, Tang H-J, Luo X-T, et al. The Prognostic Value of A Preoperative Lymphocyte Count and C-Reactive Protein Ratio. Osteosarcoma. 2021;1:65.
-
- Whelan J, Seddon B, Perisoglou M. Management of osteosarcoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2006;7:444–455. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

