Flos Carthami Exerts Hepatoprotective Action in a Rat Model of Alcoholic Liver Injury via Modulating the Metabolomics Profile
- PMID: 35547657
- PMCID: PMC9085312
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8158699
Flos Carthami Exerts Hepatoprotective Action in a Rat Model of Alcoholic Liver Injury via Modulating the Metabolomics Profile
Abstract
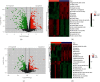
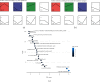
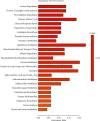
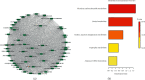
This study was intended to identify the shifts in the metabolomics profile of the hepatic tissue damaged by alcohol consumption and verify the potential restorative action of flos carthami (the flowers of Carthamus tinctorius, FC) in the protection of alcohol-induced injury by attenuating the level of identified metabolites. Rats were treated with FC and subsequently subjected to alcohol administration. The serum samples were subjected to liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS)-based metabolomics followed by statistical and bioinformatics analyses. The clustering of the samples showed an obvious separation in the principal component analysis (PCA) plot, and the scores plot of the orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) model allowed the distinction among the three groups. Among the 3211 total metabolites, 1088 features were significantly different between the control and alcohol-treated groups, while 367 metabolites were identified as differential metabolites between the alcohol- and FC-treated rat groups. Time series clustering approach indicated that 910 metabolites in profile 6 were upregulated by alcohol but subsequently reversed by FC treatment; among them, the top 10 metabolites based on the variable importance in projection (VIP) scores were 1-methyladenine, phenylglyoxylic acid, N-acetylvaline, mexiletine, L-fucose, propylthiouracil, dopamine 4-sulfate, isoleucylproline, (R)-salsolinol, and monomethyl phthalate. The Pearson correlation analysis and network construction revealed 96 hub metabolites that were upregulated in the alcohol liver injury model group but were downregulated by FC. This study confirmed the hepatoprotective effects of FC against alcohol-induced liver injury and the related changes in the metabolic profiles, which will contribute to the understanding and the treatment of alcohol-induced acute liver injury.
Copyright © 2022 Xiaojing Fan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
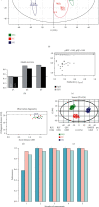
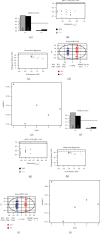
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

