Actin and Diseases of the Nervous System
- PMID: 35547659
- PMCID: PMC9088176
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7368-9_11
Actin and Diseases of the Nervous System
Abstract
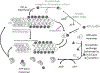
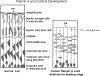
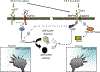
Abnormal regulation of the actin cytoskeleton results in several pathological conditions affecting primarily the nervous system. Those of genetic origin arise during development, but others manifest later in life. Actin regulation is also affected profoundly by environmental factors that can have sustained consequences for the nervous system. Those consequences follow from the fact that the actin cytoskeleton is essential for a multitude of cell biological functions ranging from neuronal migration in cortical development and dendritic spine formation to NMDA receptor activity in learning and alcoholism. Improper regulation of actin, causing aggregation, can contribute to the neurodegeneration of amyloidopathies, such as Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. Much progress has been made in understanding the molecular basis of these diseases.
Keywords: Actin-depolymerizing factor; Alzheimer; Cofilin; Down’s syndrome; Neurodegeneration; Rod.
Figures



References
-
- Allbritton NL, Meyer T, Stryer L (1992) Range of messenger action of calcium ion and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science 258:1812–1815. - PubMed
-
- Andrianantoandro E, Pollard TD (2006) Mechanism of actin filament turnover by severing and nucleation at different concentrations of ADF/cofilin. Mol Cell 24:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Ankarcrona M, Dypbukt JM, Bonfoco E, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S, Lipton SA, Nicotera P (1995) Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron 15:961–973. - PubMed
-
- Antonova I, Arancio O, Trillat AC, Wang HG, Zablow L, Udo H, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD (2001) Rapid increase in clusters of presynaptic proteins at onset of long-lasting potentiation. Science 294:1547–1550. - PubMed
-
- Ashworth SL, Southgate EL, Sandoval RM, Meberg PJ, Bamburg JR, Molitoris BA (2003) ADF/cofilin mediates actin cytoskeletal alterations in LLC-PK cells during ATP depletion. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F852–F862. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
