Crystal structure of 4-bromo- N-(propyl-carbamo-yl)benzene-sulfonamide
- PMID: 35547791
- PMCID: PMC9069509
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022003723
Crystal structure of 4-bromo- N-(propyl-carbamo-yl)benzene-sulfonamide
Abstract
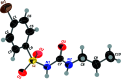
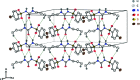
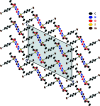
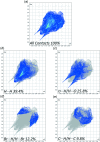
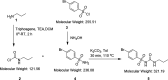
The title compound, C10H13BrN2O3S, 1, contains a sulfonyl urea moiety, which possesses potential therapeutic functions (e.g., anti-diabetic and herbicidal). The geometry of 1 is similar to its closely related analogues, chlorpropamide and tolbutamide. This compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group C2/c, having one mol-ecule in its asymmetric unit. The crystal structure of 1, recorded at 296 K, shows inter-molecular N-H⋯O and C-H⋯O-type infinite hydrogen-bonded chains involving the sulfonyl urea moiety. Hirshfeld surface analysis and the two-dimensional fingerprint plots confirmed hydrogen bonding as the dominant feature in the crystal packing.
Keywords: bromopropamide; crystal structure; single-crystal XRD; structural analogue.
© Bookwala et al. 2022.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmed, M. N., Arif, M., Jabeen, F., Khan, H. A., Yasin, K. A., Tahir, M. N., Franconetti, A. & Frontera, A. (2019). New J. Chem. 43, 8122–8131.
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–S19.
-
- Anana, R., Rao, P. P. N., Chen, Q. H. & Knaus, E. E. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14, 5259–5265. - PubMed
-
- Bieszczad, B., Siwek, A., Wilczek, M., Trzybiński, D., Woźniak, K., Satała, G., Bojarski, A. J. & Mieczkowski, A. (2020). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 30, Article 127493. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
