Hdh-Tektin-4 Regulates Motility of Fresh and Cryopreserved Sperm in Pacific Abalone, Haliotis discus hannai
- PMID: 35547812
- PMCID: PMC9081794
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.870743
Hdh-Tektin-4 Regulates Motility of Fresh and Cryopreserved Sperm in Pacific Abalone, Haliotis discus hannai
Abstract
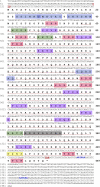
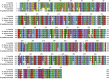
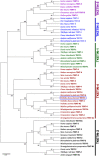
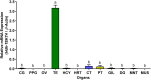
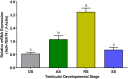
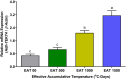
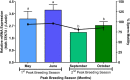
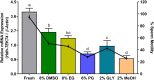
As structural components of sperm, tektins are thought to play a fundamental role in sperm flagellar motility. In this study, Tektin-4 (Hdh-TEKT4) gene was successfully cloned and characterized from the testis tissue in Pacific abalone, Haliotis discus hannai. The full-length cDNA of Hdh-TEKT4 was 1,983 bp, with a coding region of 1,350 bp encoding 51.83 kDa putative protein of 449 deduced amino acids. Hdh-TEKT4 contains a tektin domain including a nonapeptide signature motif (RPGVDLCRD). Fluorescence in situ hybridization revealed that Hdh-TEKT4 localized in the spermatids of Pacific abalone testis. qRT-PCR analysis showed that Hdh-TEKT4 was predominantly expressed in testis tissues. Hdh-TEKT4 mRNA expression was upregulated during the fully mature testicular developmental stage in both seasonal development and EAT exposed abalone. Furthermore, mRNA expression of Hdh-TEKT4 was significantly higher in sperm with higher motility than in sperm with lower motility during peak breeding season, induced spawning activity stages, and after cryopreservation in different cryoprotectants. Taken together, these results indicate that the expression of Hdh-TEKT4 in Pacific abalone sperm might have a positive correlation with sperm motility.
Keywords: Haliotis discus hannai; Pacific abalone; Tektin-4; cryopreservation; motility; sperm.
Copyright © 2022 Sukhan, Hossen, Cho, Lee and Kho.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification and Characterization of Hdh-FMRF2 Gene in Pacific Abalone and Its Possible Role in Reproduction and Larva Development.Biomolecules. 2023 Jan 5;13(1):109. doi: 10.3390/biom13010109. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36671494 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic Anhydrase in Pacific Abalone Haliotis discus hannai: Characterization, Expression, and Role in Biomineralization.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 15;8:655115. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.655115. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33937335 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-5 (IGFBP-5) Gene and Its Potential Roles in Ontogenesis in the Pacific Abalone, Haliotis discus hannai.Biology (Basel). 2020 Aug 9;9(8):216. doi: 10.3390/biology9080216. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32784850 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and structural analysis of Hdh-MIRP3 and its impact on reproductive regulation in female Pacific abalone, Haliotis discus hannai.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;263(Pt 2):130352. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130352. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38403211
-
Genetic features of Haliotis discus hannai by infection of vibrio and virus.Genes Genomics. 2020 Feb;42(2):117-125. doi: 10.1007/s13258-019-00892-w. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Genes Genomics. 2020. PMID: 31776802 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Characterization of Hdh-FMRF2 Gene in Pacific Abalone and Its Possible Role in Reproduction and Larva Development.Biomolecules. 2023 Jan 5;13(1):109. doi: 10.3390/biom13010109. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36671494 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of Tropomyosin and Its Potential Involvement in Muscle Contraction in Pacific Abalone.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 20;14(1):2. doi: 10.3390/genes14010002. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36672743 Free PMC article.
-
Gonadotropins and Sex Steroid Hormones in Captive-Reared Small Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) and Their Role in Female Reproductive Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 17;24(10):8919. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108919. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240265 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Dependent Growth-Related QTL Variations in Pacific Abalone, Haliotis discus hannai.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 29;24(17):13388. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713388. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686194 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization, Expression Analysis, and CRISPR/Cas9 Mediated Gene Disruption of Myogenic Regulatory Factor 4 (MRF4) in Nile Tilapia.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Dec 4;46(12):13725-13745. doi: 10.3390/cimb46120820. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39727948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amparyup P., Klinbunga S., Jarayabhand P. (2010). Identification and Expression Analysis of Sex-specific Expression Markers of Thai AbaloneHaliotis Asinina, Linneaus, 1758. J. Shellfish Res. 29, 765–773. 10.2983/035.029.0331 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

