Indirect study of the effect of α-tocopherol and acetylsalicylic acid on the mineral composition of bone tissue in the offspring of female rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo- p-dioxin: long-term observations
- PMID: 35547832
- PMCID: PMC9087305
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra10485a
Indirect study of the effect of α-tocopherol and acetylsalicylic acid on the mineral composition of bone tissue in the offspring of female rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo- p-dioxin: long-term observations
Abstract
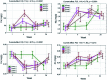
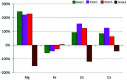
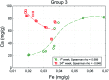
This paper discusses problems related to the influence of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on the mineral composition of the calvaria in the offspring of female rats. The female rats were administered with a single dose of TCDD and subsequently, after three-weeks, with α-tocopherol or acetylsalicylic acid. The research focused on analysis of the main mineral elements (Ca, Mg, Fe, Zn). The aim of the study was to determine the effect of dioxins and various doses of drugs on bone mineral composition in a six-month observation period. The mineral composition was analyzed using an atomic spectrometry method. Data were statistically analyzed and verified at a significance level of p = 0.05. The use of α-tocopherol normalizes bone resorption and formation disturbed by TCDD, maintaining the content of the studied elements at the physiological level. In turn, administration of acetylsalicylic acid limits the bone resorption process, which affects the element content.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Dobrzynski M. Calkosinski I. Przywitowska I. et al., Effects of dioxins in environmental pollution on development of tooth disorders. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2009;18(3):319–323.
-
- Calkosinski I. Rosinczuk-Tonderys J. Szopa M. Dobrzynski M. Gamian A. High doses of tocopherol in the prevention and potentiation of dioxin in experimental inflammation - potential application. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2011;65:143–157. doi: 10.5604/17322693.935120. doi: 10.5604/17322693.935120. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dobrzynski M., The influence of tocopherol and acetylsalicylic acid on tooth organ structure in offspring of rat dams undergoing 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), Doctoral thesis, Wroclaw Medical University, 2012
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

