Characterization of Immune-Related Genes and Immune Infiltration Features in Epilepsy by Multi-Transcriptome Data
- PMID: 35547834
- PMCID: PMC9084924
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S360743
Characterization of Immune-Related Genes and Immune Infiltration Features in Epilepsy by Multi-Transcriptome Data
Abstract
Background: Epilepsy encompasses a group of heterogeneous brain diseases that afflict about 1% of the world's population. Accumulating evidence shows that the immune system plays a key role in epileptogenesis. Nevertheless, the immune-related mechanisms remain not been precisely understood.
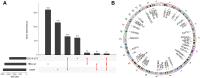
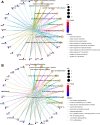
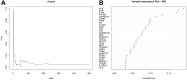
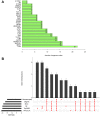
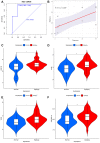
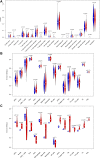
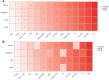
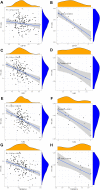
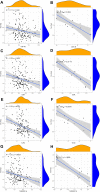
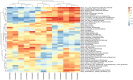
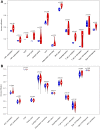
Methods: Three epilepsy datasets (GSE16969, GSE32534 and GSE143272) were screened to obtain differentially expressed immune-related genes (DEIRGs). Random forest (RF) and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network were constructed to identify core genes. Another dataset (GSE31718) and 60 clinical samples via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) were utilized to validate core genes. Immune cell infiltration score was performed with CIBERSORTx tools and single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA). Gene set variation analysis (GSVA) and ssGSEA were conducted to determine the pathways that are significantly enriched during normal and epilepsy. The correlation between hub genes, immune cells, and enriched molecular pathways was evaluated by Pearson correlation analysis.
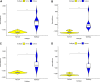
Results: Based on RF and PPI, 4 DEIRGs (CSF1R, IL6R, TLR2, and TNFRSF1A) were identified as hub genes. Results of qRT-PCR validated that higher expression levels of CSF1R, IL6R, TLR2, and TNFRSF1A in epilepsy samples compared to control sample. Immune infiltration analysis by CIBERSORTx displayed immune signatures that are significantly richer in epilepsy, T cell subsets in particular. Notably, ssGSEA found that Th1 signatures were more abundant in normal tissues; yet Th2 signatures were more abundant in epilepsy tissues. Cytokine cytokine receptor interaction (CCR) was significantly enriched in epilepsy based on multi-transcriptome data. Additionally, hub genes were significantly correlated with score of Th1/Th2 signatures and enrichment score of CCR in multi-transcriptome data.
Conclusion: Four IRGs (CSF1R, IL6R, TLR2, and TNFRSF1A) were closely correlated pathogenesis of epilepsy, which may be by impacting CCR and the balance of Th1/Th2 signatures involved in the occurrence of epilepsy. Our data offer compelling insights into the pathogenesis and promising therapeutic targets for epilepsy.
Keywords: CCR; Th1/Th2 signatures; epilepsy; immune infiltration; immune-related genes.
© 2022 Hou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Epilepsy Factsheet. WHO Webpage; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy. Accessed October 16, 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

