Serum IL-6 Level Predicts the Prognosis and Diagnosis in Cervical Cancer Patients
- PMID: 35547839
- PMCID: PMC9081182
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S347740
Serum IL-6 Level Predicts the Prognosis and Diagnosis in Cervical Cancer Patients
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) has been reported to be associated with the prognosis of cancers. As for cervical cancer (CC), previous studies investigated the association between IL-6 expression in CC tumor tissue and CC prognosis; however, no studies assessed the effects of serum IL-6 levels on the survival of CC. This study aimed to explore the effects of serum IL-6 levels on prognosis in patients with CC.
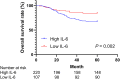
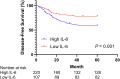
Methods: In total, 327 patients with CC and 355 controls were recruited from this hospital from May 2015 to May 2016. Serum IL-6 levels were measured before treatment. The Kaplan-Meier method was utilized to estimate survival rates. The overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) were evaluated. The univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were used to identify risk factors associated with the prognosis of CC.
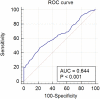
Results: We found that the serum IL-6 level in the CC group was significantly higher than that in the control group. The diagnostic value of serum IL-6 level in detecting CC patients was moderate, and the specificity and sensitivity were 77.46% and 47.09%, respectively. Data suggested that the serum IL-6 level was significantly linked with the smoking status, FIGO stage, tumor size, treatment methods, and HPV infection. The univariate and multivariate analysis indicated that FIGO stage IIB-IIIC, lymph node metastasis, and high serum IL-6 levels were negatively associated with the OS and DFS in patients with CC.
Conclusion: Serum IL-6 has a moderate diagnostic ability for detecting CC and may be a potential CC biomarker. High serum IL-6 level is associated with adverse prognosis in patients with CC and could be a prognosis indicator for CC patients.
Keywords: cervical cancer; diagnosis; interleukin-6; prognosis.
© 2022 Cai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of miR-3653 is Associated with HPV Infection and Serves as a Biomarker in Patients with Cervical Cancer.Int J Womens Health. 2022 Aug 8;14:1037-1045. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S357140. eCollection 2022. Int J Womens Health. 2022. PMID: 35966402 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio, a potential prognostic factor for patients with stage IB-IIA cervical cancer.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jul 25;20(1):691. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07191-8. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32711484 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of CCDC34 Is Associated with Poor Survival in Cervical Cancer Patients.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Nov 20;24:8383-8390. doi: 10.12659/MSM.913346. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30458457 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of IL-1α and IL-6 is Associated with Progression and Prognosis of Human Cervical Cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Nov 20;22:4475-4481. doi: 10.12659/msm.898569. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27866212 Free PMC article.
-
Better or Worse? The Independent Prognostic Role of HPV-16 or HPV-18 Positivity in Patients With Cervical Cancer: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 7;10:1733. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01733. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33117670 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Phytochemical α-Mangostin Inhibits Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth by Downregulating E6/E7-HPV Oncogenes and KCNH1 Gene Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 3;24(3):3055. doi: 10.3390/ijms24033055. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769377 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Inflammation Depending on the Stage of Cervical Cancer.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Feb 20;60(3):349. doi: 10.3390/medicina60030349. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38541074 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile of interleukin-6, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, and hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α in women with breast cancer and their association with clinicopathological parameters.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2023;27(1):14-21. doi: 10.5114/wo.2023.127199. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2023. PMID: 37266334 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 as a Pan-Cancer Prognostic Inflammatory Biomarker: A Population-Based Study and Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jan 13;18:573-587. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S484962. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39831196 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukins in the Pathogenesis of Warts: Insight from the Last Decade-A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 18;14(6):2057. doi: 10.3390/jcm14062057. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40142865 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

