Synthesis, antitumor activity and molecular mechanism of doxorubicin conjugated trimethyl-chitosan polymeric micelle loading Beclin1 siRNA for drug-resisted bladder cancer therapy
- PMID: 35547901
- PMCID: PMC9087860
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra06548a
Synthesis, antitumor activity and molecular mechanism of doxorubicin conjugated trimethyl-chitosan polymeric micelle loading Beclin1 siRNA for drug-resisted bladder cancer therapy
Abstract
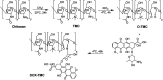
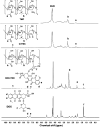
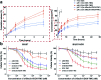
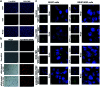
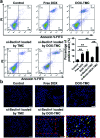
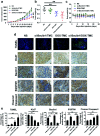
Herein, we describe a convenient approach for the preparation of a polymeric micelle using doxorubicin (DOX) conjugated trimethyl-chitosan (TMC) with Beclin-1 siRNA (Si-Beclin1/DOX-TMC). This micelle displayed a potent capacity for autophagy inhibition and reversed drug-resistance to DOX in BIU-87/ADR cell lines. The Si-Beclin1/DOX-TMC micelle was highly cytotoxic to both drug-sensitive BIU-87 and drug-resistant BIU-87/ADR cells. Its capacity to reverse drug-resistance was dependent upon upregulation of autophagy levels in BIU-87/ADR cells. DOX was conjugated to TMC via a pH-sensitive Schiff base, which responded to the acidic lysosome microenvironment and resulted in the cytoplasmic release of DOX. The structure of DOX conjugation to the TMC polymeric micelle was characterized by NMR, GPC, TEM and DLS. DOX release profiles in different pH environment were determined by HPLC. Cellular uptake, changes to nuclei morphology and formation of autophagosomes were observed using a fluorescence microscope. Finally, in vivo antitumor activity of systemic Si-Beclin1/DOX-TMC micelle administration was evaluated in BIU-87/ADR xenograft models and Si-Beclin1/DOX-TMC micelles showed significantly suppressed tumor growth.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Co-delivery of the autophagy inhibitor si-Beclin1 and the doxorubicin nano-delivery system for advanced prostate cancer treatment.J Biomater Appl. 2022 Feb;36(7):1317-1331. doi: 10.1177/08853282211060252. Epub 2021 Dec 2. J Biomater Appl. 2022. PMID: 34856824
-
Synthesis and antitumor activity of doxorubicin conjugated stearic acid-g-chitosan oligosaccharide polymeric micelles.Biomaterials. 2009 Dec;30(36):6955-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.09.008. Epub 2009 Sep 25. Biomaterials. 2009. PMID: 19782395
-
Co-delivery of doxorubicin and interleukin-2 via chitosan based nanoparticles for enhanced antitumor efficacy.Acta Biomater. 2017 Jan 1;47:81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.012. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27729232
-
pH-sensitive doxorubicin-conjugated prodrug micelles with charge-conversion for cancer therapy.Acta Biomater. 2018 Apr 1;70:186-196. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.02.008. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29452272
-
pH-responsive selenium nanoparticles stabilized by folate-chitosan delivering doxorubicin for overcoming drug-resistant cancer cells.Carbohydr Polym. 2018 Feb 1;181:841-850. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.068. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Carbohydr Polym. 2018. PMID: 29254044
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology in Bladder Cancer: Diagnosis and Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 5;13(9):2214. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092214. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

