Antibacterial properties of electrospun Ti3C2T z (MXene)/chitosan nanofibers
- PMID: 35547922
- PMCID: PMC9087880
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra06274a
Antibacterial properties of electrospun Ti3C2T z (MXene)/chitosan nanofibers
Abstract
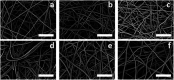
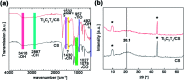
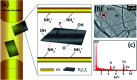
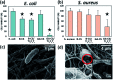
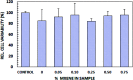
Electrospun natural polymeric bandages are highly desirable due to their low-cost, biodegradability, non-toxicity and antimicrobial properties. Functionalization of these nanofibrous mats with two-dimensional nanomaterials is an attractive strategy to enhance the antibacterial effects. Herein, we demonstrate an electrospinning process to produce encapsulated delaminated Ti3C2T z (MXene) flakes within chitosan nanofibers for passive antibacterial wound dressing applications. In vitro antibacterial studies were performed on crosslinked Ti3C2T z /chitosan composite fibers against Gram-negative Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) - demonstrating a 95% and 62% reduction in colony forming units, respectively, following 4 h of treatment with the 0.75 wt% Ti3C2T z - loaded nanofibers. Cytotoxicity studies to determine biocompatibility of the nanofibers indicated the antibacterial MXene/chitosan nanofibers are non-toxic. The incorporation of Ti3C2T z single flakes on fiber morphology was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy equipped with an energy-dispersive detector (TEM-EDS). Our results suggest that the electrospun Ti3C2T z /chitosan nanofibers are a promising candidate material in wound healing applications.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial properties of novel double layer nanocomposite electrospun fibers for wound dressing applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Mar 21;12:2205-2213. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S123417. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28356737 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of chitosan/silk fibroin composite nanofibers for wound-dressing applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 Sep 21;11(9):3529-39. doi: 10.3390/ijms11093529. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20957110 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial wound dressing from chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers mats embedded with silver nanoparticles.J Biomater Appl. 2015 Mar;29(8):1086-95. doi: 10.1177/0885328214554665. Epub 2014 Oct 2. J Biomater Appl. 2015. PMID: 25281643
-
Polysaccharide Electrospun Nanofibers for Wound Healing Applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Sep 6;17:3913-3931. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S371900. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36097445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MXene-Embedded Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications: Recent Advances.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Jul 23;14(7):1477. doi: 10.3390/mi14071477. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37512788 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unleashing the Potential of MXene-Based Flexible Materials for High-Performance Energy Storage Devices.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jan;11(3):e2304874. doi: 10.1002/advs.202304874. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 37939293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MXene: A wonderful nanomaterial in antibacterial.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 1;12:1338539. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1338539. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38361792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MXene-based composites against antibiotic-resistant bacteria: current trends and future perspectives.RSC Adv. 2023 Mar 24;13(14):9665-9677. doi: 10.1039/d3ra01276j. eCollection 2023 Mar 20. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36968045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MXene (Ti3C2Tx)-Embedded Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: A Review.Materials (Basel). 2022 Feb 23;15(5):1666. doi: 10.3390/ma15051666. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35268907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial MXenes: An emerging non-antibiotic paradigm for surface engineering of orthopedic and dental implants.Bioact Mater. 2025 May 12;51:150-176. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.05.002. eCollection 2025 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40475083 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

