Mixed valency in ligand-bridged diruthenium frameworks: divergences and perspectives
- PMID: 35547993
- PMCID: PMC9084559
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra03206h
Mixed valency in ligand-bridged diruthenium frameworks: divergences and perspectives
Abstract
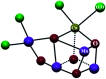
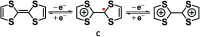
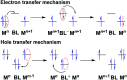
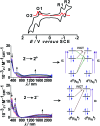
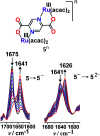
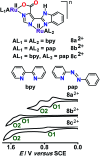
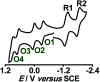
The present review article illustrates the mixed valence aspects of ligand-bridged symmetric and unsymmetric diruthenium complexes beyond the textbook example of the Creutz-Taube ion as well as the Robin and Day classification by citing representative examples based on our recent observations. The consideration of varied coordination situations involving bridging and ancillary ligands of diverse electronic and steric demands extended important fundamental events including (i) the influence of ancillary ligands besides the bridge in the intermetallic coupling process, (ii) varying profile of the intervalence charge transfer (IVCT) transition in RuIIIRuII (d5d6) and RuIIIRuIV (d5d4) mixed valence set up, (iii) divergence between the electrochemical (K c = comproportionation constant) and electronic (IVCT) coupling and (iv) occurrence of the hybrid class II-class III situation. Furthermore, additional challenges due to the introduction of redox non-innocent ligands in assigning valence and spin distributions at the metal-ligand interface as well as in differentiating the emerging alternatives of the radical-derived state and the mixed valence situation along the redox chain have been addressed.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
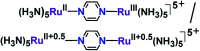






References
-
- Brown D. B., Mixed Valency Systems—Applications in Chemistry, Physics and Biology, ed. K. Prassides, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 1991
- Nelsen S. F. Chem.–Eur. J. 2000;6:581. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3765(20000218)6:4<581::AID-CHEM581>3.0.CO;2-E. - DOI - PubMed
- Aguirre-Etcheverry P. O'Hare D. Chem. Rev. 2010;110:4839. doi: 10.1021/cr9003852. - DOI - PubMed
- Low P. J. Brown N. J. J. Cluster Sci. 2010;21:235. doi: 10.1007/s10876-010-0328-4. - DOI
- Chisholm M. H. Lear B. J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011;40:5254. doi: 10.1039/C1CS15061H. - DOI - PubMed
- Hildebrandt A. Lang H. Organometallics. 2013;32:5640. doi: 10.1021/om400453m. - DOI
- Kaim W. Klein A. Glöckle M. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000;33:755. doi: 10.1021/ar960067k. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miller L. L. Mann K. R. Acc. Chem. Res. 1996;29:417. doi: 10.1021/ar9600446. - DOI
- Sun D.-L. Rosokha S. V. Lindeman S. V. Kochi J. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:15950. doi: 10.1021/ja037867s. - DOI - PubMed
- Casado J. Takimiya K. Otsubo T. Ramirez F. J. Quirante J. J. Ortiz R. P. Gonzalez S. R. Oliva M. M. Navarrete J. T. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:14028. doi: 10.1021/ja806207j. - DOI - PubMed
- Cornelis D. Franz E. Asselberghs I. Clays K. Verbiest T. Koeckelberghs G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:1317. doi: 10.1021/ja104978t. - DOI - PubMed
- Jagtap S. P. Mukhopadhyay S. Coropceanum V. Brizius G. L. Bredas J.-L. Collard D. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:7176. doi: 10.1021/ja3019065. - DOI - PubMed
- Schneebeli S. T. Frasconi M. Liu Z. Wu Y. Gardner D. M. Strutt N. L. Cheng C. Carmieli R. Wasielewski M. R. Stoddart J. F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013;52:13100. doi: 10.1002/anie.201307984. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krewald V. Retegan M. Cox N. Messinger J. Lubitz W. DeBeer S. Neese F. Pantazis D. A. Chem. Sci. 2015;6:1676. doi: 10.1039/C4SC03720K. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Klauss A. Haumann M. Dau H. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2012;109:16035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206266109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Roelofs T. A. Liang W. Latimer M. J. Cinco R. M. Rompel A. Andrews J. C. Sauer K. Yachandra V. K. Klein M. P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1996;93:3335–3340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3335. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beinert H. Holm R. H. Münck E. Science. 1997;277:653. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5326.653. - DOI - PubMed
- Subramanian S. Duin E. C. Fawcett S. E. J. Armstrong F. A. Meyer J. Johnson M. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015;137:4567. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b01869. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Rumpel S. Siebel J. F. Diallo M. FarÀs C. Reijerse E. J. Lubitz W. ChemBioChem. 2015;16:1663–1669. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201500130. - DOI - PubMed
- Pandelia M.-E. Bykov D. Izsak R. Infossi P. Orticoni M.-T. G. Bill E. Neese F. Lubitz W. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013;110:483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1202575110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

