Contextual Factors and Motor Skills in Indigenous Amazon Forest and Urban Indigenous Children
- PMID: 35548073
- PMCID: PMC9082032
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.858394
Contextual Factors and Motor Skills in Indigenous Amazon Forest and Urban Indigenous Children
Abstract
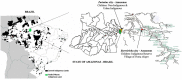
This study investigated the contextual factors, motor performance, and body mass index across indigenous land children, indigenous urban children, and non-indigenous urban children. A number of 153 children, both sexes (71 girls, 46.4%), from 8 to 10 years were assessed. The Test of Motor Gross Development-3 was utilized. Indigenous land children showed higher motor performance ( = 0.37 and = 0.19 locomotor and object control, respectively) than indigenous urban children (p < 0.03) and non-indigenous urban children (p < 0.01); Indigenous urban children showed higher motor performance than non-indigenous urban children (p < 0.01). Body mass index was similar across groups ( = 0,02; p = 0.15). Motor performance of indigenous land children was explained by the contextual factors that lead to a more active lifestyle, unsupervised free time, and play outside. In urban areas, behavior was similar, and although indigenous urban children kept some play tradition, it was not strong enough to be a protective factor for the motor performance.
Keywords: child development; children; ethnical groups; indigenous peoples; motor skills.
Copyright © 2022 Duarte, Valentini, Nobre and Benda.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abarca-Gómez L, Abdeen ZA, Hamid ZA, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Acosta-Cazares B, Acuin C, et al. . Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. (2017) 390:2627–42. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Selbacha RS, Schaab DM, Berlesea DB, Sanfelicea GR. Relationship between motor development and the nutritional status of schools in a city of Vale dos Sinos Region, RS, Brazil. J Health Sci. (2021) 23:327–33. 10.17921/2447-8938.2021v23n4p327-333 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

