Numerical simulations of wall contact angle effects on droplet size during step emulsification
- PMID: 35548132
- PMCID: PMC9086337
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra06837b
Numerical simulations of wall contact angle effects on droplet size during step emulsification
Abstract
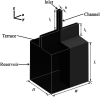
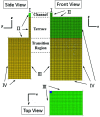
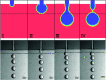
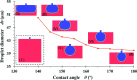
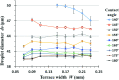
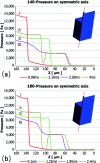
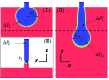
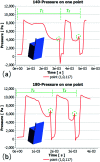
Terrace-based microfluidic devices are currently used to prepare highly monodisperse micro-droplets. Droplets are generated due to the spontaneous pressure drop induced by the Laplace pressure, and so the flow rate of a dispersed phase has little effect on droplet size. As a result, control over the droplet is limited once a step emulsification device has been fabricated. In this work, a terrace model was established to study the effect of the wall contact angle on droplet size based on computational fluid dynamics simulations. The results for contact angles from 140° to 180° show that a lower contact angle induces wall-wetting, increasing the droplet size. The Laplace pressure equations for droplet generation were determined based on combining pressure change curves with theoretical analyses, to provide a theoretical basis for controlling and handling droplets generated through step emulsification.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

