Comparative study on synchronous adsorption of arsenate and fluoride in aqueous solution onto MgAlFe-LDHs with different intercalating anions
- PMID: 35548142
- PMCID: PMC9086567
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra05968c
Comparative study on synchronous adsorption of arsenate and fluoride in aqueous solution onto MgAlFe-LDHs with different intercalating anions
Abstract
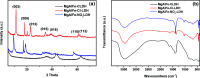
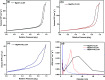
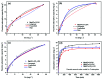
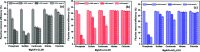
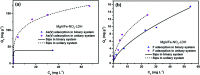
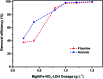
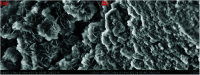
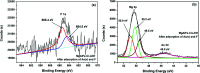
In this study, a series of MgAlFe-LDHs (Cl-, NO3 -, intercalation, and calcined products of a CO3 2- interlayer) was synthesized and used for adsorption of arsenate and fluoride in individual contaminants and coexisting pollutant systems. Effects of various factors such as initial pH of solution, dosage of materials, coexisting ions, contact time, and initial pollutant concentrations were evaluated. Experimental results showed that different intercalating anions had a significant effect on adsorption performance of arsenate and fluoride in water. The adsorption of arsenate and fluoride on MgAlFe-CLDH, MgAlFe-Cl-LDH or MgAlFe-NO3-LDH can be described by different adsorption isotherm equations. During the simultaneous removal process, arsenate and fluoride competed for adsorption sites of the adsorbent materials, and the fluoride ions had advantages in the competitive adsorption on MgAlFe-Cl-LDH and MgAlFe-NO3-LDH. MgAlFe-NO3-LDH was used to adsorb arsenate and fluoride in coexisting pollution systems (the concentration of each pollutant was 2 mg L-1, the adsorbent dosage was 1.5 g L-1). The remaining arsenic concentration was reduced to less than 10 μg L-1 and the remaining fluoride ion concentration to below 20 μg L-1 which meets the World Health Organization's, EPA's and China's drinking water standards for arsenic and fluoride limits. A possible mechanism is discussed with support from further XRD, SEM, and XPS analysis of the materials after their adsorption.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures








References
-
- Khair A. M. Li C. C. Hu Q. H. Gao X. B. Wanga Y. X. Geochem. Int. 2014;52:868–881. doi: 10.1134/S0016702914100024. - DOI
-
- Gonzalez-Horta C. Ballinas-Casarrubias L. Sanchez-Ramirez B. Ishida M. C. Barrera-Hernandez A. Gutierrez-Torres D. Zacarias O. L. Saunders R. J. Drobna Z. Mendez M. A. Garcia-Vargas G. Loomis D. Styblo M. Del Razo L. M. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2015;12:4587–4601. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120504587. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shahab A. Qi S. Zaheer M. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018 doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2320-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

