Functionalization of boron-doped diamond with a push-pull chromophore via Sonogashira and CuAAC chemistry
- PMID: 35548149
- PMCID: PMC9086440
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra07545j
Functionalization of boron-doped diamond with a push-pull chromophore via Sonogashira and CuAAC chemistry
Abstract
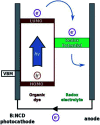
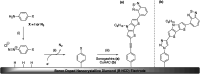
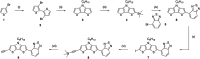
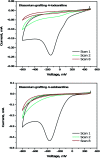
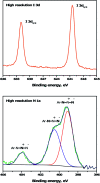
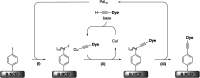
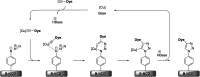
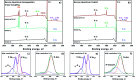
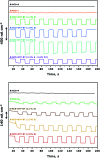
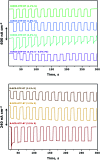
Improving the performance of p-type photoelectrodes represents a key challenge toward significant advancement in the field of tandem dye-sensitized solar cells. Herein, we demonstrate the application of boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond (B:NCD) thin films, covalently functionalized with a dithienopyrrole-benzothiadiazole push-pull chromophore, as alternative photocathodes. First, a primary functional handle is introduced on H-terminated diamond via electrochemical diazonium grafting. Afterwards, Sonogashira cross-coupling and Cu(i) catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) reactions are employed to attach the chromophore, enabling the comparison of the degree of surface functionalization and the importance of the employed linker at the diamond-dye interface. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy shows that surface functionalization via CuAAC results in a slightly higher chromophore coverage compared to the Sonogashira cross-coupling. However, photocurrents and photovoltages, obtained by photoelectrochemical and Kelvin probe measurements, are approximately three times larger on photocathodes functionalized via Sonogashira cross-coupling. Surface functionalization via Sonogashira cross-coupling is thus considered the preferential method for the development of diamond-based hybrid photovoltaics.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

