Transient Receptor Potential Channel 1 Potentially Serves as a Biomarker Indicating T/TNM Stages and Predicting Long-Term Prognosis in Patients With Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 35548183
- PMCID: PMC9081676
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.853310
Transient Receptor Potential Channel 1 Potentially Serves as a Biomarker Indicating T/TNM Stages and Predicting Long-Term Prognosis in Patients With Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Transient receptor potential channel 1 (TRPC1) regulates the progression of several cancers, but its clinical implication in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has not been explored yet. This study aimed to investigate the correlation of TRPC1 with clinical characteristics and prognosis in patients with RCC.
Methods: Totally, 177 patients with primary RCC who received surgical resection were retrospectively screened. Their tumor and paired adjacent tissue specimens were retrieved to assess TRPC1 mRNA expression using RT-qPCR and TRPC1 protein expression using immunohistochemistry (IHC).
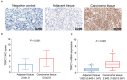
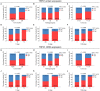
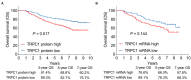
Results: Both TRPC1 IHC score and TRPC1 mRNA expression were elevated in RCC tissue than in adjacent tissue (both P < 0.001). Meanwhile, both TRPC1 IHC score and TRPC1 mRNA expression in tumor were associated with higher T stage (both P = 0.02) and TNM stage (P = 0.009, P = 0.003, respectively). However, no correlation was found in tumor TRPC1 IHC score or TRPC1 mRNA expression with other tumor properties (all P > 0.05). Besides, the 3-, 5-, and 7-year overall survival (OS) were 81.4, 68.6, and 60.2%, respectively in patients with high tumor TRPC1 protein, while they were 89.3, 82.7, and 76.7%, respectively in patients with low tumor TRPC1 protein. High (vs. low) TRPC1 protein in the tumor was associated with shorter OS (P = 0.017), while high (vs. low) TRPC1 mRNA in the tumor was not correlated with OS (P = 0.144). By the forward stepwise method, TRPC1 protein expression independently predicted poor OS (P = 0.01, hazard ratio = 2.052).
Conclusion: TRPC1 serves as a potential biomarker reflecting tumor features and long-term survival profile in patients with RCC.
Keywords: T stage; TNM stage; overall survival; renal cell carcinoma; transient receptor potential channel 1.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Shan, Ge, Qian and Xia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arora RD, Limaiem F. Renal Clear Cell Cancer. StatPearls Treasure Island (FL) (2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

