Ameliorative effects and possible molecular mechanisms of action of fibrauretine from Fibraurea recisa Pierre on d-galactose/AlCl3-mediated Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 35548215
- PMCID: PMC9085853
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra05356a
Ameliorative effects and possible molecular mechanisms of action of fibrauretine from Fibraurea recisa Pierre on d-galactose/AlCl3-mediated Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
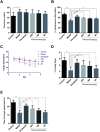
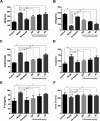
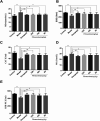
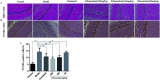
Fibrauretine is one of the main active ingredients from the rattan stems of Fibraurea recisa Pierre It exhibits a series of significant pharmacological effects. The present study aimed to evaluate the potential anti Alzheimer's disease (AD) effects of fibrauretine on a d-galactose/AlCl3-induced mouse model, and the underlying mechanisms of action were further investigated for the first time. Our results showed that pretreatment with fibrauretine significantly improved the ability of spatial short-term working memory in the model mice during the Y-maze test, as well as the abilities of spatial learning and memory during the Morris water maze. The levels of brain tissue amyloid (Aβ), P-Tau, Tau and acetylcholinesterase (AchE) were evidently increased in d-galactose/AlCl3-intoxicated mice, and these effects were reversed by fibrauretine. In contrast, a significant increase in the levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (Ach) and choline acetyl transferase (ChAT) was observed in the fibrauretine-treated groups compared with the model group. Neuronal oxidative stress, evidenced by increased malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitric oxide (NO) levels and a decline in glutathione (GSH), catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, was significantly alleviated by fibrauretine pretreatment. The suppression of the neuroinflammatory response by fibrauretine was realized not only by the decrease in the levels of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in the brain tissues and by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) but also by the protein expression levels of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), which were measured by immunohistochemistry and western blotting. In addition, the protein expression levels of inflammatory factors interleukin-33 (IL-33) and ST2 in the brain tissues were detected by immunohistochemistry. Furthermore, the effects of western blotting demonstrated that the administration of fibrauretine significantly suppressed the protein expression levels of caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3, and Bax and increased the protein expression levels of Bcl-2, and the results of the H&E and TUNEL assay all suggested the inhibition of apoptosis in the neurons. The results clearly suggest that the underlying molecular mechanisms of action of the fibrauretine-mediated alleviation of d-galactose/AlCl3-induced Alzheimer's disease may involve antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cognitive-enhancing effects of fibrauretine on Aβ1-42-induced Alzheimer's disease by compatibilization with ginsenosides.Neuropeptides. 2020 Aug;82:102020. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2020.102020. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Neuropeptides. 2020. PMID: 31982159
-
Protective effects of kinetin against aluminum chloride and D-galactose induced cognitive impairment and oxidative damage in mouse.Brain Res Bull. 2017 Sep;134:262-272. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Brain Res Bull. 2017. PMID: 28867383
-
Barbaloin's Chemical Intervention in Aluminum Chloride Induced Cognitive Deficits and Changes in Rats through Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Cytokines, and BDNF Expression.ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 29;9(6):6976-6985. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08791. eCollection 2024 Feb 13. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38371830 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of deoxygedunin on Alzheimer-like pathologic dysfunction induced by D-galactose combined with AlCl3].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Jun 8;34(6):496-500. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.5732.2018.111. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 31032583 Chinese.
-
Ameliorative effect of myrcene in mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 15;911:174529. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174529. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34592305
Cited by
-
Antidepressant effects of total alkaloids of Fibraurea recisa on improving corticosterone-induced apoptosis of HT-22 cells and chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviour in mice.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1436-1448. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2099429. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35938494 Free PMC article.
-
Prominent Effects of Berbamine Hydrochloride on Alzheimer's Disease Model Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 30;13:939039. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.939039. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35846991 Free PMC article.
-
Centella asiatica Protects d-Galactose/AlCl3 Mediated Alzheimer's Disease-Like Rats via PP2A/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway in Their Hippocampus.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 16;20(8):1871. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081871. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31014012 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic roles of plants for 15 hypothesised causal bases of Alzheimer's disease.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2022 Aug 23;12(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s13659-022-00354-z. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2022. PMID: 35996065 Free PMC article.
-
D‑galactose induces astrocytic aging and contributes to astrocytoma progression and chemoresistance via cellular senescence.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Nov;20(5):4111-4118. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10677. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31545444 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

