Alpinumisoflavone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating the effects of anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation both in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 35548248
- PMCID: PMC9085634
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra04098b
Alpinumisoflavone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating the effects of anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation both in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
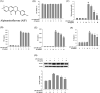
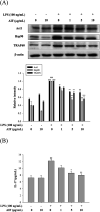
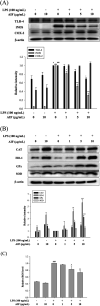
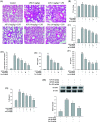
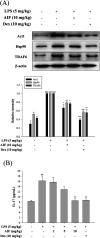
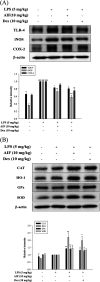
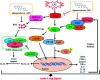
Alpinumisoflavone (AIF) is a plant-derived pyranoisoflavone that exhibits a number of pharmacological activities, but the protective effects of AIF against pulmonary inflammation are still unknown. This study aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects and possible molecular mechanisms of AIF in both lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages and mice. The results revealed that AIF dramatically suppressed the production of pro-inflammatory mediators [including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, IL-17, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and nitric oxide (NO)] and increased the levels of anti-oxidative enzymes [including catalase (CAT), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and superoxide dismutase (SOD)] both in vitro and in vivo. Additionally, pre-treatment with AIF could not only significantly prevent histopathological changes and neutrophil infiltration but also decreased the expression levels of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), and the nucleotide-binding domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, as well as IL-17 production in LPS-induced lung tissues. The anti-inflammatory effects of AIF were mediated by up-regulating anti-oxidative enzymes and suppressing the NF-κB, MAPK, NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-17 signaling pathways. This is the first study to reveal that AIF has a protective effect against LPS-induced lung injury in mice.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Baskar N. Devi B. P. Kumar R. M. Anti-cancer activity of methanol extract of root bark of Erythrina variegata Linn. International Journal of Toxicological and Pharmacological Research. 2010;2:74–76.
-
- Namkoong S. Kim T. J. Jang I. S. Kang K. W. Oh W. K. Park J. Alpinumisoflavone induces apoptosis and suppresses extracellular signal-regulated kinases/mitogen activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB pathways in lung tumor cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011;34:203–208. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.203. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kingsford-Adaboh R. Dittrich B. Hübschle C. B. Gbewonyo W. S. Okamoto H. Kimura M. Ishida H. Invariom structure refinement, electrostatic potential and toxicity of 4-O-methylalpinumisoflavone, O,O-dimethylalpinumisoflavone and 5-O-methyl-4-O-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)alpinumisoflavone. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci. 2006;62:843–849. doi: 10.1107/S0108768106019616. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

