Managing Musculoskeletal and Kidney Aging: A Call for Holistic Insights
- PMID: 35548383
- PMCID: PMC9081621
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S357501
Managing Musculoskeletal and Kidney Aging: A Call for Holistic Insights
Abstract
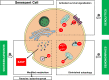
Aging represents a major concern, with a two-fold increase in individuals >65 years old by 2040. Older patients experience multiple declines in condition, with overlapping concerns. Fractures, frailty and falls remain underestimated events in routine practice. They are shared by numerous conditions and diseases, such as osteoporosis, sarcopenia and undernutrition, which mostly feature low evolution and are silent. In this review, we focused on musculoskeletal decline in older individuals who also have chronic kidney disease (CKD), which promotes fractures and falls. We aimed to highlight the need for a global approach for musculoskeletal and kidney aging. Although strategies limiting falls remain controversial, the need for an early diagnosis can limit these declines and allow for specific treatment of bone fragility in addition to non-pharmacological approaches. The emergence of senolytic agents offers new hope for preventing musculoskeletal disorders. This scoping review describes these overlapping silent diseases, provides evidence for their global understanding and management, and sheds light on new therapeutic directions.
Keywords: kidney disease; older individuals; osteoporosis; sarcopenia; senolytics.
© 2022 Cailleaux and Cohen-Solal.
Conflict of interest statement
Pierre-Emmanuel Cailleaux declares that he has no competing interest. Martine Cohen-Solal declares that she has no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Beaudart C, Rolland Y, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, et al. Assessment of muscle function and physical performance in daily clinical practice: a position paper endorsed by the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO). Calcif Tissue Int. 2019;105:1–14. doi:10.1007/s00223-019-00545-w - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

