Anticancer activities of a β-amino alcohol ligand and nanoparticles of its copper(ii) and zinc(ii) complexes evaluated by experimental and theoretical methods
- PMID: 35548400
- PMCID: PMC9084389
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra04578j
Anticancer activities of a β-amino alcohol ligand and nanoparticles of its copper(ii) and zinc(ii) complexes evaluated by experimental and theoretical methods
Abstract
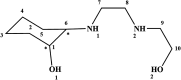
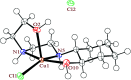
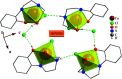
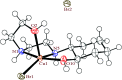
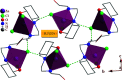
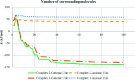
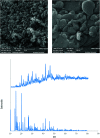
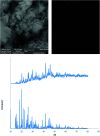
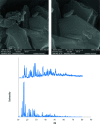
2-(2-(2-Hydroxyethylamino)ethylamino)cyclohexanol (HEAC) and copper and zinc complexes, [Cu(HEAC)Cl]Cl (1), [Cu(HEAC)Br]Br (2), [Zn(HEAC)Cl2] (3), were prepared and identified by elemental analysis, FT-IR, UV-Vis, 1H NMR spectroscopy and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Also nanoparticles of 1-3 were prepared for anticancer studies by ultrasonic irradiation. Particle size and morphology of the nano particles are investigated by PXRD and SEM, respectively. X-ray analysis revealed that the ionic complexes 1 and 2 are isostructural. In the structure of complexes 1 and 2, the metal atom has a CuN2O2X (X: Cl (1), Br (2)) environment with square-pyramidal geometry, containing the tetradentate N2O2-donor HEAC. The bond length of the axial position in the square-pyramidal geometry of 1 and 2 is elongated. Complex 3 has a ZnN2OCl2 environment with trigonal bipyramidal geometry around the zinc atom in which the HEAC acts as mer-N2O-donor. The ability of HEAC and nano particles 1-3 to interact with the nine biomacromolecules (BRAF kinase, CatB, DNA gyrase, HDAC7, rHA, RNR, TrxR, TS and Top II) are investigated by docking calculations. For examination of the docking results, the in vitro activities of four compounds against the human leukemia cell line K562 were investigated by evaluation of IC50 values and mode of cell death (apoptosis). The thermodynamic stability of the compounds along with the charge distribution pattern were studied by DFT and NBO analysis, respectively.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Theoretical and experimental investigation of anticancer activities of an acyclic and symmetrical compartmental Schiff base ligand and its Co(ii), Cu(ii) and Zn(ii) complexes.RSC Adv. 2018 Oct 17;8(62):35625-35639. doi: 10.1039/c8ra07463a. eCollection 2018 Oct 15. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35547928 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of a triazine ligand with CuII and AgI investigated by spectral, structural, theoretical and docking studies.Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2019 Oct 1;75(Pt 10):1389-1397. doi: 10.1107/S2053229619011719. Epub 2019 Sep 7. Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2019. PMID: 31589155
-
Reaction of 2-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]ethanol with pyridine-2-carbaldehyde and complexation of the products with CuII and CdII along with docking studies.Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2019 Jul 1;75(Pt 7):951-959. doi: 10.1107/S2053229619008258. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2019. PMID: 31271384
-
Investigation of the effect of the N-oxidation process on the interaction of selected pyridine compounds with biomacromolecules: structural, spectral, theoretical and docking studies.Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2019 Jun 1;75(Pt 6):750-757. doi: 10.1107/S2053229619006375. Epub 2019 May 22. Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2019. PMID: 31166929
-
Water soluble Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes of bidentate-morpholine based ligand: synthesis, spectral, DFT calculation, biological activities and molecular docking studies.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Feb;40(3):1074-1083. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1821783. Epub 2020 Sep 16. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 32936064
Cited by
-
Zinc Complexes with Nitrogen Donor Ligands as Anticancer Agents.Molecules. 2020 Dec 9;25(24):5814. doi: 10.3390/molecules25245814. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33317158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, characterization and anticancer activities of Zn2+, Cu2+, Co2+ and Ni2+ complexes involving chiral amino alcohols.RSC Adv. 2022 Nov 9;12(49):32119-32128. doi: 10.1039/d2ra05576g. eCollection 2022 Nov 3. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36415554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kwon S. J. Ko S. Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002;43:639–641. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)02206-7. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

