Etiology and Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients With Cancer
- PMID: 35548413
- PMCID: PMC9081373
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.892335
Etiology and Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients With Cancer
Abstract
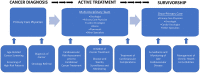
Patients with cancer are now living longer than ever before due to the growth and expansion of highly effective antineoplastic therapies. Many of these patients face additional health challenges, of which cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading contributor to morbidity and mortality. CVD and cancer share common biological mechanisms and risk factors, including lipid abnormalities. A better understanding of the relationship between lipid metabolism and cancer can reveal strategies for cancer prevention and CVD risk reduction. Several anticancer treatments adversely affect lipid levels, increasing triglycerides and/or LDL-cholesterol. The traditional CVD risk assessment tools do not include cancer-specific parameters and may underestimate the true long-term CVD risk in this patient population. Statins are the mainstay of therapy in both primary and secondary CVD prevention. The role of non-statin therapies, including ezetimibe, PCSK9 inhibitors, bempedoic acid and icosapent ethyl in the management of lipid disorders in patients with cancer remains largely unknown. A contemporary cancer patient needs a personalized comprehensive cardiovascular assessment, management of lipid abnormalities, and prevention of late CVD to achieve optimal overall outcomes.
Keywords: cancer; cancer survivor; cardiovascular risk reduction; cholesterol; dyslipidemia.
Copyright © 2022 de Jesus, Mohammed, Singh, Tiu and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aparecida Silveira E, Vaseghi G, de Carvalho Santos AS, Kliemann N, Masoudkabir F, Noll M, et al. . Visceral Obesity and Its Shared Role in Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease: a Scoping Review of the Pathophysiology and Pharmacological Treatments. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:E9042. 10.3390/ijms21239042 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous