Nationwide Initiation of Cardiovascular Risk Treatments During the COVID-19 Pandemic in France: Women on a Slippery Slope?
- PMID: 35548431
- PMCID: PMC9081923
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.856689
Nationwide Initiation of Cardiovascular Risk Treatments During the COVID-19 Pandemic in France: Women on a Slippery Slope?
Abstract
Objectives: This study examines the initiation of prescribed medication treatments for cardiovascular risk (antihypertensives, lipid-lowering drugs, oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation, and smoking cessation medications) during the COVID-19 pandemic in the French population.
Methods: For each year between 2017 and 2021, we used the French National Insurance Database to identify the number of people with at least one reimbursement for these medications but no reimbursement in the previous 12 months. We computed incidence rate ratios (IRRs) between 2017-2019 and, respectively 2020 and 2021 using Poisson regression adjusted for age and 2017-2019 time trends. We recorded the number of lipid profile blood tests, Holter electrocardiograms, and consultations with family physicians or cardiologists.
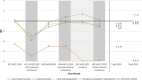
Results: In 2020, IRR significantly decreased for initiations of antihypertensives (-11.1%[CI95%, -11.4%;-10.8%]), lipid-lowering drugs (-5.2%[CI95%, -5.5%;-4.8%]), oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation (-8.6%[CI95%, -9.1%;-8.0%]), and smoking cessation medications (-50.9%[CI95%, -51.1%;-50.7%]) compared to 2017-2019. Larger decreases were found in women compared to men except for smoking cessation medications, with the sex difference increasing with age. Similar analyses comparing 2021 to 2017-2019 showed an increase in the initiation of lipid-lowering drugs (+ 11.6%[CI95%, 10.7%;12.5%]) but even lower rates for the other medications, particularly in women. In addition, the 2020 number of people visiting a family physician or cardiologist decreased by 8.4 and 7.4%. A higher decrease in these visits was observed in those over 65 years of age compared to those under 65 years of age. A greater use of teleconsultation was found in women.
Conclusion: The COVID-19 pandemic heavily impacted the initiation of medication treatments for cardiovascular risk in France, particularly in women and people over 65 years.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; cardiovascular; cardiovascular risk; initiation; medication.
Copyright © 2022 Gabet, Grave, Tuppin, Lesuffleur, Guenancia, Nguyen-Thanh, Guignard, Blacher and Olié.
Conflict of interest statement
CGu reported, outside the submitted work, grants from Microport CRM, consulting fees from Boston Scientific and Microport CRM, and honoraria from Medtronic. JB reports, outside the submitted work, personal fees from Abbott, Bayer, Bottu, Ferring, Steripharma, Kantar, Teriak, personal fees and non-financial support from Pfizer, Quantum Genomics, personal fees from Sanofi and Servier. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Utilization of DXA Bone Mineral Densitometry in Ontario: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(20):1-180. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074491 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in initiation of direct oral anticoagulant therapies for atrial fibrillation in a national population-based cross-sectional study in the French health insurance databases.BMJ Open. 2018 Mar 30;8(3):e018180. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018180. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29602837 Free PMC article.
-
[Drawing up guidelines for the attendance of physical health of patients with severe mental illness].Encephale. 2009 Sep;35(4):330-9. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2008.10.014. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Encephale. 2009. PMID: 19748369 French.
-
Association Between Use of Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants With and Without Concurrent Medications and Risk of Major Bleeding in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation.JAMA. 2017 Oct 3;318(13):1250-1259. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.13883. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28973247 Free PMC article.
-
[Cost-effectiveness analysis of schizophrenic patient care settings: impact of an atypical antipsychotic under long-acting injection formulation].Encephale. 2005 Mar-Apr;31(2):235-46. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(05)82390-5. Encephale. 2005. PMID: 15959450 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Underuse of primary healthcare in France during the COVID-19 epidemic in 2020 according to individual characteristics: a national observational study.BMC Prim Care. 2022 Aug 9;23(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12875-022-01792-x. BMC Prim Care. 2022. PMID: 35945511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davin-Casalena B, Jardin M, Guerrera H, Mabille J, Tréhard H, Lapalus D, et al. [The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on first-line primary care in Southeastern France: feedback on the implementation of a real-time monitoring system based on regional health insurance data]. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. (2021) 69:105–15. 10.1016/j.respe.2021.04.135 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

