Blood Flow Restriction Resistance Training in Tendon Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review on Intervention Parameters, Physiological Effects, and Outcomes
- PMID: 35548459
- PMCID: PMC9083008
- DOI: 10.3389/fspor.2022.879860
Blood Flow Restriction Resistance Training in Tendon Rehabilitation: A Scoping Review on Intervention Parameters, Physiological Effects, and Outcomes
Abstract
Objective: To identify current evidence on blood flow restriction training (BFRT) in tendon injuries and healthy tendons, evaluating physiological tendon effects, intervention parameters, and outcomes.
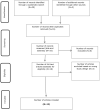
Methods: This scoping review was reported in accordance with the PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR). Databases searched included MEDLINE, CINAHL, AMED, EMBase, SPORTDiscus, Cochrane library (Controlled trials, Systematic reviews), and five trial registries. Two independent reviewers screened studies at title/abstract and full text. Following screening, data was extracted and charted, and presented as figures and tables alongside a narrative synthesis. Any study design conducted on adults, investigating the effects of BFRT on healthy tendons or tendon pathology were included. Data were extracted on physiological tendon effects, intervention parameters and outcomes with BFRT.
Results: Thirteen studies were included, three on tendinopathy, two on tendon ruptures, and eight on healthy Achilles, patellar, and supraspinatus tendons. A variety of outcomes were assessed, including pain, function, strength, and tendon morphological and mechanical properties, particularly changes in tendon thickness. BFRT intervention parameters were heterogeneously prescribed.
Conclusion: Despite a dearth of studies to date on the effects of BFRT on healthy tendons and in tendon pathologies, preliminary evidence for beneficial effects of BFRT on tendons and clinical outcomes is encouraging. As BFRT is a relatively novel method, definitive conclusions, and recommendations on BFRT in tendon rehabilitation cannot be made at present, which should be addressed in future research, due to the potential therapeutic benefits highlighted in this review.
Keywords: blood flow restriction; exercise; physiotherapy; resistance training; tendinopathy; tendon.
Copyright © 2022 Burton and McCormack.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
-
- Abe T., Sakamaki M., Fujita S., Ozaki H., Sugaya M., Sato Y., et al. (2010b). Effects of low-intensity walk training with restricted leg blood flow on muscle strength and aerobic capacity in older adults. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 33, 34–40. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials