Role of Non-Coding RNA in Neurological Complications Associated With Enterovirus 71
- PMID: 35548469
- PMCID: PMC9081983
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.873304
Role of Non-Coding RNA in Neurological Complications Associated With Enterovirus 71
Abstract
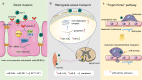
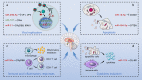
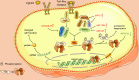
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is the main pathogenic virus that causes hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). Studies have reported that EV71-induced infections including aseptic meningitis, acute flaccid paralysis, and even neurogenic pulmonary edema, can progress to severe neurological complications in infants, young children, and the immunosuppressed population. However, the mechanisms through which EV71 causes neurological diseases have not been fully explored. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), are RNAs that do not code for proteins, play a key role in biological processes and disease development associated with EV71. In this review, we summarized recent advances concerning the impacts of ncRNAs on neurological diseases caused by interaction between EV71 and host, revealing the potential role of ncRNAs in pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of EV71-induced neurological complications.
Keywords: and mouse disease; enterovirus 71; foot; hand; long non-coding RNA; microRNA; non-coding RNA; virus-host interaction.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Zhang, Chen, Yin, Xu, Cheng, Ma, Meng and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

