Apology and Its Acceptance: Perceived Reconciliatory Attitudes Reduce Outgroup Dehumanization
- PMID: 35548505
- PMCID: PMC9083360
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.809513
Apology and Its Acceptance: Perceived Reconciliatory Attitudes Reduce Outgroup Dehumanization
Abstract
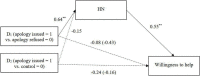
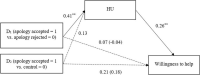
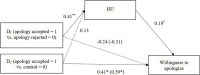
Based on real-life intergroup animosities originating from a historical conflict, the current study examined how the perceived stance of the outgroup about the conflict affects the dehumanization of the outgroup. In Study 1 (N = 120), Korean undergraduates attributed more human nature to the Japanese after reading an article that the Japanese government did (vs. refused to) issue an official apology for a historical wrong. In turn, the more human nature assigned to the Japanese predicted higher expectations about positive mutual relations in the future. Similarly, in Study 2 (N = 209), Japanese undergraduates attributed more human uniqueness to Koreans after reading an article that an official apology for a historical wrong from Japan was accepted (vs. rejected) by Koreans. The higher the perceived human uniqueness of Koreans was, the higher were the willingness to help and the expectations of a positive relationship in the future. The findings demonstrate how mutual dehumanization can be reduced as a result of the other side's reconciliatory stances and can further contribute to improving intergroup relations.
Keywords: acceptance; apology; historical conflict; human nature; human uniqueness; intergroup relations.
Copyright © 2022 Jin, Park and Park.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human-itarian aid? Two forms of dehumanization and willingness to help after natural disasters.Br J Soc Psychol. 2014 Sep;53(3):573-84. doi: 10.1111/bjso.12066. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Br J Soc Psychol. 2014. PMID: 24588786
-
They see us as less than human: Metadehumanization predicts intergroup conflict via reciprocal dehumanization.J Pers Soc Psychol. 2016 Mar;110(3):343-70. doi: 10.1037/pspa0000044. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2016. PMID: 26963763
-
A social virus: Intergroup dehumanization and unwillingness to aid amidst COVID-19 - Who are the main targets?Int J Intercult Relat. 2022 Jan;86:109-121. doi: 10.1016/j.ijintrel.2021.11.006. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Int J Intercult Relat. 2022. PMID: 34866714 Free PMC article.
-
Dehumanization and the lack of social connection.Curr Opin Psychol. 2022 Feb;43:312-316. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2021.08.013. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022. PMID: 34517201 Review.
-
Dehumanization: an integrative review.Pers Soc Psychol Rev. 2006;10(3):252-64. doi: 10.1207/s15327957pspr1003_4. Pers Soc Psychol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16859440 Review.
Cited by
-
Mediating and moderating effects of perceived social support on the relationship between discrimination and well-being: A study of South Koreans living in Japan.Front Psychol. 2022 Jul 28;13:922201. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.922201. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35967623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bain P., Park J., Kwok C., Haslam N. (2009). Attributing human uniqueness and human nature to cultural groups: distinct forms of subtle dehumanization. Group Proc. Intergr. Relat. 12 789–805. 10.1177/1368430209340415 - DOI
-
- Bandura A., Underwood B., Fromson M. E. (1975). Disinhibition of aggression through diffusion of responsibility and dehumanization of victims. J. Res. Pers. 9 253–269. 10.1016/0092-6566(75)90001-X - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

