Adolescents' Algorithmic Resistance to Short Video APP's Recommendation: The Dual Mediating Role of Resistance Willingness and Resistance Intention
- PMID: 35548508
- PMCID: PMC9083067
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.859597
Adolescents' Algorithmic Resistance to Short Video APP's Recommendation: The Dual Mediating Role of Resistance Willingness and Resistance Intention
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Adolescents' algorithmic resistance to short video APP's recommendation: the dual mediating role of resistance willingness and resistance intention.Front Psychol. 2025 Aug 7;16:1675601. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1675601. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40851569 Free PMC article.
Abstract
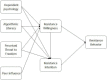
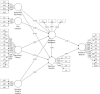
Adolescents have gradually become a vital group of interacting with social media recommendation algorithms. Although numerous studies have been conducted to investigate negative reactions (both psychological and behavioral reactance) that the dark side of recommendation algorithms brings to social media users, little is known about the resistance intention and behavior based on their agency in the daily process of encountering algorithms. Focusing on the concept of algorithm resistance, this study used a two-path model (distinguishing resistance willingness and resistance intention) to investigate the algorithmic resistance of rural Chinese adolescents (N = 905) in their daily use of short video apps. The findings revealed that the perceived threat to freedom, algorithmic literacy, and peer influence were positively associated with the resistance willingness and intention; while the independent psychology on algorithmic recommendations significantly weakened resistance willingness and intention. Furthermore, this study verified the mediating role of resistance willingness and intention between the above independent variables and resistance behavior. Additionally, the positive impact of resistance willingness on resistance intention was confirmed. In conclusion, this study offers a comprehensive approach to further understanding adolescents' algorithmic resistance awareness and behavior by combining psychological factors, personal competency, and interpersonal influences, as well as two types of resistance reactions (rational and irrational).
Keywords: Chinese rural adolescent; algorithmic literacy; algorithmic resistance; recommendation algorithm; short video APP.
Copyright © 2022 Lv, Chen and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arriagada A., Ibáñez F. (2020). “You need at least one picture daily, if not, you’re dead”: content creators and platform evolution in the social media ecology. Soc. Media Soc. 6:205630512094462. 10.1177/2056305120944624 - DOI
-
- Ajzen I., Madden T. J. (1986). Prediction of goal-directed behavior: attitudes, intentions, and perceived behavioral control. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 22 453–474.
-
- Baier A. (1986). Trust and Antitrust. Ethics 96(2), 231–260. 10.1086/292745 - DOI
-
- Ball-Rokeach S. J., DeFleur M. L. (1976). A dependency model of mass-media effects. Commun. Res. 3 3–21. 10.1177/009365027600300101 - DOI
-
- Bandy J., Diakopoulos N. (2021). Curating quality? how twitter’s timeline algorithm treats different types of news. Soc. Media Soc. 7:205630512110416. 10.1177/20563051211041648 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources