Comparison of the Impacts of a Dynamic Exercise Program vs. a Mediterranean Diet on Serum Cytokine Concentrations in Women With Rheumatoid Arthritis. A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 35548581
- PMCID: PMC9082589
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.834824
Comparison of the Impacts of a Dynamic Exercise Program vs. a Mediterranean Diet on Serum Cytokine Concentrations in Women With Rheumatoid Arthritis. A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease characterized by a chronic inflammatory state. High pro-inflammatory cytokine levels are associated with disease activity. Exercise and the Mediterranean diet (MD) exert anti-inflammatory effects; however, their impacts on inflammation in RA patients remains unknown. This study aimed to compare the effects of six-months of dynamic exercise program (DEP) vs. MD on pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine serum concentrations.
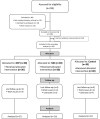
Methods: Secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial in which 90 women with RA were randomly assigned to the DEP (n = 30), MD (n = 30), or control group (n = 30). All patients received pharmacological treatment. Serum concentrations of pro-inflammatory (TNF-α, TNF-β, IL-1β, IL-6 pg/mL) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10, IL-Ra pg/mL) cytokines were measured at baseline and after 6 months using the Luminex technique.
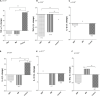
Results: After 6 months of follow-up, we found an improvement of the median percentages changes concentrations of TNF-α (DEP, -12.3; MD, -13.3; control, 73.2; p = 0.01), TNF-β (DEP, -67.4; MD, -54.9; control, 0; p = 0.04), and IL-6 (DEP, -19.9; MD, -37.7; control, 45.5; p = 0.04) in the DEP and MED groups in comparison with control group. IL-1Ra concentrations increased only in the MD group (13.8) compared to levels in the control group (-31.7), p = 0.04. There were no statistically significant differences between DEP and MD groups. Only n = 27 participants in the DEP group, n = 26 in the MD group, and n = 21 in the control group completed the follow-up.
Conclusion: The DEP and the MD have potential effects in the concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines compared with those in a control group. Only the MD elevated the concentration of IL-Ra.
Clinical trial registration: [ClinicalTrials.gov], identifier [NCT02900898].
Keywords: clinical trial; cytokines; exercise program; mediterranean diet; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2022 Lozada-Mellado, Llorente, Hinojosa-Azaola, García-Morales, Ogata-Medel, Alcocer-Varela, Pineda-Juárez and Castillo-Martínez.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62:2569–81. - PubMed
-
- Grassi W, De Angelis R, Lamanna G, Cervini C. The clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Radiol. (1998) 27:S18–24. - PubMed
-
- Gibofsky A. Overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Manag Care. (2012) 18:S295–302. - PubMed
-
- Weissmann G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. (2006) 64:12–5. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

