Andrographolide inhibits human serum albumin fibril formations through site-specific molecular interactions
- PMID: 35548768
- PMCID: PMC9085492
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra04637a
Andrographolide inhibits human serum albumin fibril formations through site-specific molecular interactions
Abstract
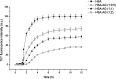
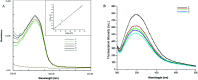
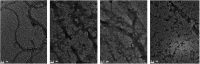
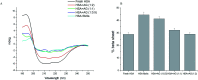
Protein misfolding and fibrillation are the fundamental traits in degenerative diseases like Alzheimer's, Parkinsonism, and diabetes mellitus. Bioactives such as flavonoids and terpenoids from plant sources are known to express protective effects against an array of diseases including diabetes, Alzheimer's and obesity. Andrographolide (AG), a labdane diterpenoid is prescribed widely in the Indian and Chinese health care systems for classical efficacy against a number of degenerative diseases. This work presents an in depth study on the effects of AG on protein fibrillating pathophysiology. Thioflavin T fluorescence spectroscopy and DLS results indicated concentration dependent inhibition of human serum albumin (HSA) fibrillation. The results were confirmed by electron microscopy studies. HSA fibril formations were markedly reduced in the presence of AG. Fluorescence studies and UV-Vis experiments confirmed further that AG molecularly interacts with HSA at site. In silico molecular docking studies revealed hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions with HSA in the native state. Thus AG interacts with HSA, stabilizes the native protein structure and inhibits fibrillation. The results demonstrated that the compound possesses anti-amyloidogenic properties and can be promising against some human degenerative diseases.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors would also like to acknowledge that there is no conflict of interest in publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Chaturvedi S. K. Siddiqi M. K. Alam P. Khan R. H. Process Biochem. 2016;51:1183–1192. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2016.05.015. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

