Transcriptional analysis of long non-coding RNAs in facet joint osteoarthritis
- PMID: 35548800
- PMCID: PMC9086565
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra04809f
Transcriptional analysis of long non-coding RNAs in facet joint osteoarthritis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Transcriptional analysis of long non-coding RNAs in facet joint osteoarthritis.RSC Adv. 2018 Oct 18;8(62):35689. doi: 10.1039/c8ra90079e. eCollection 2018 Oct 15. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35567466 Free PMC article.
Abstract
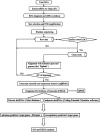
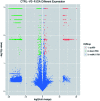
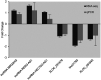
It is recognized that facet joint osteoarthritis (FJOA) is commonly induced by the degeneration of articular cartilage of the facet joint. However, the specific pathological mechanisms underlying facet joint osteoarthritis has not yet been elucidated. To obtain the differential expression patterns and putative functions of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in FJOA, in the current study, we detected the expression levels of lncRNAs in patients with varying degrees of facet cartilage degeneration (control group: normal or mild facet cartilage degeneration; FJOA: moderate to severe facet cartilage degeneration) by RNA deep sequencing. Differentially expressed lncRNAs were screened and the accuracy of sequencing data was further validated by using quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Target genes of differentially expressed lncRNAs were predicted by antisense and/or cis-regulatory module prediction. Predicted target genes were further analyzed by Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Enrichment of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis (KEGG) to discover enriched cellular component, molecular function, biological process, and signaling pathways. Our results provided a general view of the expression changes of lncRNAs in FJOA and thus might facilitate the illumination of the underlying mechanisms of FJOA.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Sun H. L. Yun S. J. Jo H. H. Dong H. K. Song J. G. Yong S. P. Skeletal Radiol. 2017:1–14.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

