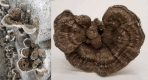
A review of the phytochemical and pharmacological properties of Amauroderma rugosum
- PMID: 35548873
- PMCID: PMC11896323
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12554
A review of the phytochemical and pharmacological properties of Amauroderma rugosum
Abstract
Amauroderma rugosum (AR) is a basidiomycete in the Ganodermataceae family that has been used traditionally to prevent epileptic attacks and constant crying in babies. However, AR has not been widely studied scientifically. In this review, we summarize the phytochemical components and pharmacological properties of AR that have been reported in the literature. Chemical analyses have revealed that the components of AR include sterols, flavonoids, fatty acids and esters, aromatic acids and esters, phenols, polysaccharides, and triterpenes. Pharmacological properties of AR include antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-cancer, anti-hyperlipidemic, anti-epileptic, and antibacterial effects. These findings suggest that AR and its bioactive ingredients have potential therapeutic applications, particularly for age-related diseases.
Keywords: anti-cancer; anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; pharmacology; phytochemicals.
© 2022 The Authors. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhao J, Zheng X. Polyporaceae. In: Zhì Zhong Guo Zhen Jun, editor. Editorial Committee of Book of Chinese cryptogams (Book of Chinese Funngi). 8th ed. Beijing: Science Press; 2000. [in Chinese]
-
- Taxonomy GB. Amauroderma rugosum (Blume & T.Nees) Torrend in GBIF Secretariat, 2021. Available at https://www.gbif.org/species/5248422.
-
- Bi Z, Zheng G, Li T. The macrofungus flora of China's Guangdong Province. Hong Kong, China: Chinese University Press; 1993. [in Chinese].
-
- Endemia . Amauroderma rugosum (Blume & T. Nees) Torrend. Fauna and Flora of New Caledonia, Nouméa, Nouvelle‐Calédonie: Endemia. 2022. Available at https://endemia.nc/en/fonge/fiche363.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials