Extracellular Vesicles from Hypoxic Pretreated Urine-Derived Stem Cells Enhance the Proliferation and Migration of Chondrocytes by Delivering miR-26a-5p
- PMID: 35548888
- PMCID: PMC9137301
- DOI: 10.1177/19476035221077401
Extracellular Vesicles from Hypoxic Pretreated Urine-Derived Stem Cells Enhance the Proliferation and Migration of Chondrocytes by Delivering miR-26a-5p
Abstract
Objective: Stem-cell therapy is a promising treatment for cartilage defects. The newly identified urine-derived stem cells (USCs), which have multipotency and sufficient proliferative ability, are promising candidates for several tissue engineering therapies. In this study, we investigated the role of USC extracellular vehicles (EVs) in promoting the proliferation and migration of chondrocytes.
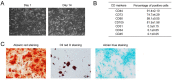
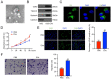
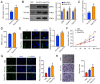
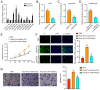
Design: USCs were characterized by measuring induced multipotent differentiation and flow cytometry analysis of surface marker expression. The EVs were isolated from USCs under normoxic conditions (nor-EVs) and hypoxic conditions (hypo-EVs). Transmission electron microscopy and western blot analysis characterized the EVs. The chondrocytes were cultured in the USC-EVs. CCK-8 assay and EdU staining detected the proliferation of chondrocytes, and transwell assay detected their migration. miR-26a-5p expression in EVs was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The target relationship of miR-26a-5p and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) was predicted and confirmed. The roles of EVs-miR-26a-5p and PTEN on the proliferation and migration of chondrocytes were also investigated.
Results: Hypo-EVs showed a superior effect in promoting the proliferation and migration of chondrocytes than nor-EVs. Mechanistically, USC-EVs delivered miR-26a-5p into chondrocytes to overexpress miR-26a-5p. PTEN was identified as an miR-26a-5p target in chondrocytes. The effects of EVs-miR-26a-5p on promoting the proliferation and migration of chondrocytes were mediated by its regulation of PTEN.
Conclusion: Our study suggested that hypoxic USC-EVs may represent a promising strategy for osteoarthritis by promoting the proliferation and migration of chondrocytes via miR-26a-5p transfer.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; hypoxia; miR-26a-5p; osteoarthritis; urine-derived stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles containing microRN555A-26a-5p ameliorate cartilage damage of osteoarthritis.J Gene Med. 2021 Nov;23(11):e3379. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3379. Epub 2021 Aug 11. J Gene Med. 2021. PMID: 34296780
-
Urine-derived stem cells-extracellular vesicles ameliorate diabetic osteoporosis through HDAC4/HIF-1α/VEGFA axis by delivering microRNA-26a-5p.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Oct;39(5):2243-2257. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09713-5. Epub 2022 May 13. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 35554780
-
Small-sized extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from acute myeloid leukemia bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transfer miR-26a-5p to promote acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation, migration, and invasion.Hum Cell. 2021 May;34(3):965-976. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00501-7. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 33620671
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Urine-Derived Stem Cell for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2024 Apr;30(2):176-197. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2023.0100. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2024. PMID: 37603497 Review.
-
From Bench to Bedside: The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Cartilage Injury Treatment.Biomater Res. 2024 Nov 22;28:0110. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0110. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 39583872 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Breakthrough of extracellular vesicles in pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis.Bioact Mater. 2022 Oct 20;22:423-452. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.10.012. eCollection 2023 Apr. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 36311050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies in product engineering of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: unveiling the mechanisms underpinning the promotive effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 May 2;12:1363780. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1363780. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38756412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutics of the future: Navigating the pitfalls of extracellular vesicles research from an osteoarthritis perspective.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Jul;13(7):e12435. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12435. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 38943211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urine-derived stem cells in neurological diseases: current state-of-the-art and future directions.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Oct 30;16:1229728. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1229728. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37965041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secretive derived from hypoxia preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells promote cartilage regeneration and mitigate joint inflammation via extracellular vesicles.Bioact Mater. 2023 Mar 29;27:98-112. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.03.017. eCollection 2023 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 37006826 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

