Effects of age and gender on neural correlates of emotion imagery
- PMID: 35548890
- PMCID: PMC9374878
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.25906
Effects of age and gender on neural correlates of emotion imagery
Abstract
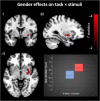
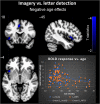
Mental imagery is part of people's own internal processing and plays an important role in everyday life, cognition and pathology. The neural network supporting mental imagery is bottom-up modulated by the imagery content. Here, we examined the complex associations of gender and age with the neural mechanisms underlying emotion imagery. We assessed the brain circuits involved in emotion mental imagery (vs. action imagery), controlled by a letter detection task on the same stimuli, chosen to ensure attention to the stimuli and to discourage imagery, in 91 men and women aged 14-65 years using fMRI. In women, compared with men, emotion imagery significantly increased activation within the right putamen, which is involved in emotional processing. Increasing age, significantly decreased mental imagery-related activation in the left insula and cingulate cortex, areas involved in awareness of ones' internal states, and it significantly decreased emotion verbs-related activation in the left putamen, which is part of the limbic system. This finding suggests a top-down mechanism by which gender and age, in interaction with bottom-up effect of type of stimulus, or directly, can modulate the brain mechanisms underlying mental imagery.
Keywords: age; emotion; fMRI; gender; imagery; limbic system.
© 2022 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander, G. E. , DeLong, M. R. , & Strick, P. L. (1986). Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 9, 357–381. - PubMed
-
- Bradley MM, Lang PJ. Affective Norms for English Words (ANEW): Instruction Manual and Affective Ratings. University of Florida; NIMH Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention; 1999.
-
- Campos, A. , & Sueiro, E. (1993). Sex and age differences in visual imagery vividness. Journal of Mental Imagery, 17, 91–94.

