The role of hypothermic machine perfusion in selecting renal grafts with advanced histological score
- PMID: 35548925
- PMCID: PMC9544822
- DOI: 10.1111/aor.14308
The role of hypothermic machine perfusion in selecting renal grafts with advanced histological score
Abstract
Background: Few studies explored the role of hypothermic machine perfusion (HMP) in the sub-group of non-standard renal grafts with a biopsy-proven advanced histological impairment. This study aimed to investigate the role of HMP in grafts with a Karpinski Score >3 in terms of the need for dialysis, creatinine reduction ratio at day-7 (CRR7), and 3-year graft survival.
Methods: Twenty-three perfused grafts with Karpinski Score >3 evaluated between November 2017 and December 2018 were retrospectively analyzed and compared with a control group of 32 non-perfused grafts transplanted between January 2014 and October 2017.
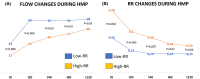
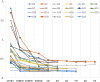
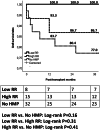
Results: After transplantation, perfused grafts had fewer cases requiring dialysis (8.7% vs. 34.4%; p = 0.051), a better reduction in serum creatinine (median at 7 days: 2.2 vs. 4.3 mg/dl; p = 0.045), and shorter length of hospital stay (median 11 vs. 15 days; p = 0.01). Three-year death-censored graft survival was better in the perfused cases (91.3% vs. 77.0%; p = 0.16). In perfused grafts, initial renal resistance (RR) had the best predictive value for renal function recovery after the first week, as defined by CRR7 ≤ 70% (AUC = 0.83; p = 0.02). A cut-off value of 0.5 mm Hg/ml/min showed a sensitivity of 82.4%, a specificity of 83.3%, and diagnostic odds ratio = 23.4. After dividing the entire population into a Low-RR (n = 8) and a High-RR Group (n = 15), more cases with CRR7 ≤ 70% were reported in the latter group (86.7 vs. 13.3%; p = 0.03).
Conclusion: HMP yielded promising results in kidneys with Karpinski Score >3. Initial RR should be of interest in selecting non-standard organs for single kidney transplantation even in impaired histology.
Keywords: Karpinski Score; delayed graft function; dialysis; graft loss; perfusion; serum creatinine.
© 2022 The Authors. Artificial Organs published by International Center for Artificial Organ and Transplantation (ICAOT) and Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare about the present study.
Figures
References
-
- Rao PS, Schaubel DE, Guidinger MK, Andreoni KA, Wolfe RA, Merion RM, et al. A comprehensive risk quantification score for deceased donor kidneys: the kidney donor risk index. Transplantation. 2009;88:231–6. - PubMed
-
- Pretagostini R, Lai Q, Poli L, Levi Sandri GB, Travaglia D, Rossi M, et al. Predictive characteristics of delayed graft function after expanded and standard criteria donor kidney transplantations. Transplant Proc. 2009;41:1149–51. - PubMed
-
- Lai Q, Nudo F, Morabito V, et al. Donor quality scoring systems and early renal function measurements in kidney transplantation. In: Ortiz J, Andre J editors. Understanding the complexities of kidney transplantation. Intech Open; 2011. 10.5772/17845 - DOI
-
- Querard AH, Foucher Y, Combescure C, Dantan E, Larmet D, Lorent M, et al. Comparison of survival outcomes between expanded criteria donor and standard criteria donor kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Transpl Int. 2016;29:403–15. - PubMed
-
- Karpinski J, Lajoie G, Cattran D, Fenton S, Zaltzman J, Cardella C, et al. Outcome of kidney transplantation from high‐risk donors is determined by both structure and function. Transplantation. 1999;67:1162–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

