Tuaimenal A, a Meroterpene from the Irish Deep-Sea Soft Coral Duva florida, Displays Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Enzyme
- PMID: 35549259
- PMCID: PMC9127705
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00054
Tuaimenal A, a Meroterpene from the Irish Deep-Sea Soft Coral Duva florida, Displays Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Enzyme
Abstract
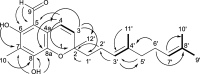
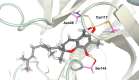
Cold water benthic environments are a prolific source of structurally diverse molecules with a range of bioactivities against human disease. Specimens of a previously chemically unexplored soft coral, Duva florida, were collected during a deep-sea cruise that sampled marine invertebrates along the Irish continental margin in 2018. Tuaimenal A (1), a cyclized merosesquiterpenoid representing a new carbon scaffold with a highly substituted chromene core, was discovered through exploration of the soft coral secondary metabolome via NMR-guided fractionation. The absolute configuration was determined through vibrational circular dichroism. Functional biochemical assays and in silico docking experiments found tuaimenal A selectively inhibits the viral main protease (3CLpro) of SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Roberts J. M.; Wheeler A.; Freiwald A.; Cairns S.. Cold-Water Corals: The Biology and Geology of Deep-Sea Coral Habitats; Cambridge University Press, 2009.
-
- Daly M.; Brugler M. R.; Cartwright P.; Collins A. G.; Dawson M. N.; Fautin D. G.; France S. C.; McFadden C. S.; Opresko D. M.; Rodriguez E.; Romano S. L.; Stake J. L. The Phylum Cnidaria: A Review of Phylogenetic Patterns and Diversity 300 Years after Linnaeus*. Zootaxa 2007, 1668 (1), 127–182. 10.11646/zootaxa.1668.1.11. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Miscellaneous

