Penicillin Derivatives Inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Reaction with Its Nucleophilic Cysteine
- PMID: 35549342
- PMCID: PMC9115881
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c02214
Penicillin Derivatives Inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Reaction with Its Nucleophilic Cysteine
Abstract
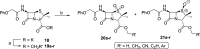
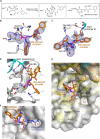
The SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) is a medicinal chemistry target for COVID-19 treatment. Given the clinical efficacy of β-lactams as inhibitors of bacterial nucleophilic enzymes, they are of interest as inhibitors of viral nucleophilic serine and cysteine proteases. We describe the synthesis of penicillin derivatives which are potent Mpro inhibitors and investigate their mechanism of inhibition using mass spectrometric and crystallographic analyses. The results suggest that β-lactams have considerable potential as Mpro inhibitors via a mechanism involving reaction with the nucleophilic cysteine to form a stable acyl-enzyme complex as shown by crystallographic analysis. The results highlight the potential for inhibition of viral proteases employing nucleophilic catalysis by β-lactams and related acylating agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
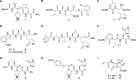
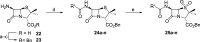

References
-
- Gorbalenya A. E.; Baker S. C.; Baric R. S.; de Groot R. J.; Drosten C.; Gulyaeva A. A.; Haagmans B. L.; Lauber C.; Leontovich A. M.; Neuman B. W.; Penzar D.; Perlman S.; Poon L. L. M.; Samborskiy D. V.; Sidorov I. A.; Sola I.; Ziebuhr J. The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. 10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

