Circular RNA_0120376 regulates microRNA-148b-3 and centrosomal protein 55 to promote non-small cell lung cancer development
- PMID: 35549631
- PMCID: PMC9275942
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2052647
Circular RNA_0120376 regulates microRNA-148b-3 and centrosomal protein 55 to promote non-small cell lung cancer development
Abstract
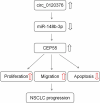
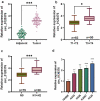
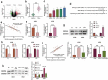
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are non-coding RNAs with covalent closed-loop structures that are vital in regulating diverse pathological processes. This work is aimed to investigate the role of circ_0120376 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Circ_0120376, microRNA (miR)-148b-3p, and centrosomal protein 55 (CEP55) mRNA expression in NSCLC tissues and cells were determined using qRT-PCR. The influences of circ_0120376 and miR-148b-3p on the proliferation of NSCLC cell lines were analyzed by CCK-8 and colony formation assays. Apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry. Cell migration and invasion were analyzed using the Transwell experiment. Binding relationships between circ_0120376 and miR-148b-3p and between miR-148b-3p and CEP55 3'UTR were investigated using the dual-luciferase reporter experiment and the RIP experiment. Western blot was conducted to analyze the regulatory effect of circ_0120376 and miR-148b-3p on CEP55 expression. We found that circ_0120376 was markedly overexpressed in NSCLC, and its overexpression was positively associated with increased T stage and lymph node metastasis of the patients. Functional experiments unveiled that circ_0120376 enhanced the proliferation, migration and invasion of NSCLC cells and impeded apoptosis, while knocking down circ_0120376 remarkably suppressed the malignant features of NSCLC cells mentioned above. Circ_0120376 could adsorb miR-148b-3p to reduce miR-148b-3p expression, and circ_0120376 could increase CEP55 expression via adsorbing miR-148b-3p. In summary, circ_0120376 contributes to the malignancy of NSCLC cells through a ceRNA mechanism via regulating miR-148b-3p/CEP55 axis. Circ_0120376 is likely to be a potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for NSCLC.
Keywords: CEP55; Circ_0120376; NSCLC; miR-148b-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



Similar articles
-
Circ_0074027 contributes to non-small cell lung cancer progression through positively modulating RHOA via sequestering miR-2467-3p.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2021 Apr;53(2):223-233. doi: 10.1007/s10863-021-09876-6. Epub 2021 Mar 9. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2021. PMID: 33687619
-
Circ_0016760 Serves as a Cancer Promoter in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Through miR-876-3p/NOVA2 Axis.Biochem Genet. 2022 Dec;60(6):2087-2105. doi: 10.1007/s10528-022-10198-4. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Biochem Genet. 2022. PMID: 35239092
-
Circular RNA-UBE2D2 accelerates the proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells via modulating microRNA-376a-3p/Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4γ2 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):5942-5953. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2027068. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35196197 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Value of miR-148b in Human Cancers.Curr Mol Med. 2022;22(10):860-869. doi: 10.2174/1566524021666211213123315. Curr Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34961461 Review.
-
A review on expression and regulatory mechanisms of miR-337-3p in cancer.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Mar 18:1-10. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2024.2329294. Online ahead of print. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 38500239 Review.
Cited by
-
CircRNA hsa_circ_0070659 predicts poor prognosis and promotes non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression via microRNA-377 (miR-377) / Ras-Associated Binding Protein 3C (RAB3C) pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 Jun;13(6):14578-14594. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2091572. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 36694911 Free PMC article.
-
CEP55 as a promising biomarker and therapeutic target on gallbladder cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 May 18;13:1156177. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1156177. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37274251 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs and Cancers.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1485:273-327. doi: 10.1007/978-981-96-9428-0_18. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40886283 Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C.. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553(7689):446–454. - PubMed
-
- Duma N, Santana-Davila R, Molina JR. Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(8):1623–1640. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Yang L, Chen LL. The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 2018;71(3):428–442. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
