Peroxiredoxin 6 mediates the protective function of curcumin pretreatment in acute lung injury induced by serum from patients undergoing one-lung ventilation in vitro
- PMID: 35549905
- PMCID: PMC9101832
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-022-01988-y
Peroxiredoxin 6 mediates the protective function of curcumin pretreatment in acute lung injury induced by serum from patients undergoing one-lung ventilation in vitro
Abstract
Background: Curcumin has attracted much attention due to its wide range of therapeutic effects. In this study, we used serum collected from patients undergoing one-lung ventilation (OLV) to establish an in vitro acute lung injury (ALI) model to explore the potential protective mechanism of curcumin on ALI. Our study provides a new reference for the prevention and treatment of ALI induced by OLV.
Methods: A549 cells were treated with 20% serum from patients undergoing OLV to establish an in vitro ALI model. Curcumin, at a dose of 40 μg/ml, was administered two hours prior to this model. The levels of inflammation and oxidative stress markers were observed by Western blot, qRT-PCR, ELISA and reactive oxygen species assay. Additionally, the expression of peroxiredoxin 6 (Prdx6) and proteins involved in the NF-κB signaling pathway was evaluated.
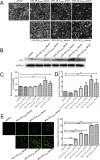
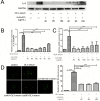
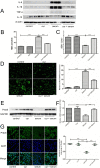
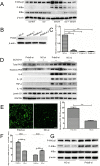
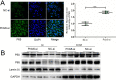
Results: Twenty percent of serum collected from patients undergoing OLV downregulated the expression of Prdx6, leading to the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which was associated with the subsequent overproduction of inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species. Pretreatment with curcumin restored Prdx6 downregulation and inhibited NF-κB pathway activation by suppressing the nuclear translocation of P65, eventually reducing inflammation and oxidative stress damage in A549 cells.
Conclusions: Prdx6 mediated the protective function of curcumin by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB pathway in ALI in vitro.
Keywords: Curcumin; Lung injury; NF-κB signaling; One-lung ventilation; Peroxiredoxin 6.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Lu Y-T, Hellewell PG, Evans TW. Ishemia-reperfusion lung injury contribution of ischemianeutrophils and hydrostatic pressure.pdf. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:46–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

