CREB5 reprograms FOXA1 nuclear interactions to promote resistance to androgen receptor-targeting therapies
- PMID: 35550030
- PMCID: PMC9135408
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.73223
CREB5 reprograms FOXA1 nuclear interactions to promote resistance to androgen receptor-targeting therapies
Abstract
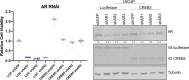
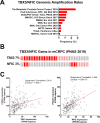
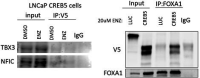
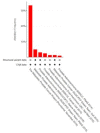
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancers (mCRPCs) are treated with therapies that antagonize the androgen receptor (AR). Nearly all patients develop resistance to AR-targeted therapies (ARTs). Our previous work identified CREB5 as an upregulated target gene in human mCRPC that promoted resistance to all clinically approved ART. The mechanisms by which CREB5 promotes progression of mCRPC or other cancers remains elusive. Integrating ChIP-seq and rapid immunoprecipitation and mass spectroscopy of endogenous proteins, we report that cells overexpressing CREB5 demonstrate extensive reprogramming of nuclear protein-protein interactions in response to the ART agent enzalutamide. Specifically, CREB5 physically interacts with AR, the pioneering actor FOXA1, and other known co-factors of AR and FOXA1 at transcription regulatory elements recently found to be active in mCRPC patients. We identified a subset of CREB5/FOXA1 co-interacting nuclear factors that have critical functions for AR transcription (GRHL2, HOXB13) while others (TBX3, NFIC) regulated cell viability and ART resistance and were amplified or overexpressed in mCRPC. Upon examining the nuclear protein interactions and the impact of CREB5 expression on the mCRPC patient transcriptome, we found that CREB5 was associated with Wnt signaling and epithelial to mesenchymal transitions, implicating these pathways in CREB5/FOXA1-mediated ART resistance. Overall, these observations define the molecular interactions among CREB5, FOXA1, and pathways that promote ART resistance.
Keywords: CREB5; FOXA1; RIME; cancer biology; chromosomes; gene expression; human; prostate cancer; therapy resistance; transcription reprogramming.
© 2022, Hwang, Arafeh, Seo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JH is a consultant for Astrin Biosciences, Principal Investigator for Caris Life Sciences Genitourinary disease working group, RA, JS, SB, ML, TA, LS, CR, ST, HB, SM, JR, SK, AC, JK, JS, SK, JD, MF No competing interests declared, EV serves as Advisory/Consulting for Tango Therapeutics, Genome Medical, Invitae, Enara Bio, Janssen, Manifold Bio, Monte Rosa, received research support from Novartis, BMS, has equity with Tango Therapeutics, Genome Medical, Syapse, Enara Bio, Manifold Bio, Microsoft, Monte Rosa, receives travel reimbursement from Roche/Genentech, and holds patents including Institutional patents filed on chromatin mutations and immunotherapy response, and methods for clinical interpretation, WH Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures







References
-
- Abida W, Cyrta J, Heller G, Prandi D, Armenia J, Coleman I, Cieslik M, Benelli M, Robinson D, Van Allen EM, Sboner A, Fedrizzi T, Mosquera JM, Robinson BD, De Sarkar N, Kunju LP, Tomlins S, Wu YM, Nava Rodrigues D, Loda M, Gopalan A, Reuter VE, Pritchard CC, Mateo J, Bianchini D, Miranda S, Carreira S, Rescigno P, Filipenko J, Vinson J, Montgomery RB, Beltran H, Heath EI, Scher HI, Kantoff PW, Taplin ME, Schultz N, deBono JS, Demichelis F, Nelson PS, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM, Sawyers CL. Genomic correlates of clinical outcome in advanced prostate cancer. PNAS. 2019;116:11428–11436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902651116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adams EJ, Karthaus WR, Hoover E, Liu D, Gruet A, Zhang Z, Cho H, DiLoreto R, Chhangawala S, Liu Y, Watson PA, Davicioni E, Sboner A, Barbieri CE, Bose R, Leslie CS, Sawyers CL. FOXA1 mutations alter pioneering activity, differentiation and prostate cancer phenotypes. Nature. 2019;571:408–412. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1318-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alumkal JJ, Sun D, Lu E, Beer TM, Thomas GV, Latour E, Aggarwal R, Cetnar J, Ryan CJ, Tabatabaei S, Bailey S, Turina CB, Quigley DA, Guan X, Foye A, Youngren JF, Urrutia J, Huang J, Weinstein AS, Friedl V, Rettig M, Reiter RE, Spratt DE, Gleave M, Evans CP, Stuart JM, Chen Y, Feng FY, Small EJ, Witte ON, Xia Z. Transcriptional profiling identifies an androgen receptor activity-low, stemness program associated with enzalutamide resistance. PNAS. 2020;117:12315–12323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922207117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armenia J, Wankowicz SAM, Liu D, Gao J, Kundra R, Reznik E, Chatila WK, Chakravarty D, Han GC, Coleman I, Montgomery B, Pritchard C, Morrissey C, Barbieri CE, Beltran H, Sboner A, Zafeiriou Z, Miranda S, Bielski CM, Penson AV, Tolonen C, Huang FW, Robinson D, Wu YM, Lonigro R, Garraway LA, Demichelis F, Kantoff PW, Taplin M-E, Abida W, Taylor BS, Scher HI, Nelson PS, de Bono JS, Rubin MA, Sawyers CL, Chinnaiyan AM, PCF/SU2C International Prostate Cancer Dream Team. Schultz N, Van Allen EM. The long tail of oncogenic drivers in prostate cancer. Nature Genetics. 2018;50:645–651. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0078-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

