Novel case of empyema necessitans caused by Mycobacterium xenopi
- PMID: 35550319
- PMCID: PMC9109015
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-245953
Novel case of empyema necessitans caused by Mycobacterium xenopi
Abstract
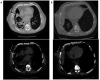
Poorly controlled long-standing empyema can dissect through soft tissues and skin resulting in empyema necessitans. We present the first reported case of empyema necessitans caused by Mycobacterium xenopi, which was treated successfully with antimycobacterial therapy. The case highlights the indolent nature of the pathogen and the importance of an accurate diagnosis.
Keywords: Empyema; Infections; Pleural infection.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium abscessus subsp. abscessus empyema complicated with subcutaneous abscess.J Infect Chemother. 2020 Feb;26(2):300-304. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2019.09.006. Epub 2019 Dec 16. J Infect Chemother. 2020. PMID: 31859040
-
[Mycobacterium xenopi: a rare mycobacterium?].Arch Bronconeumol. 2002 Aug;38(8):401-2. doi: 10.1016/s0300-2896(02)75249-6. Arch Bronconeumol. 2002. PMID: 12199926 Spanish. No abstract available.
-
Radiology corner. Answer to last month's radiology case (#43) and image: Mycobacterium xenopi found incidentally on MRI of the cervical spine.Mil Med. 2010 Jan;175(1):xvii-xviii. Mil Med. 2010. PMID: 20108848 No abstract available.
-
Prosthetic joint infection due to Mycobacterium xenopi: a review of the literature with a new case report.Infection. 2020 Apr;48(2):165-171. doi: 10.1007/s15010-019-01318-1. Epub 2019 May 16. Infection. 2020. PMID: 31098926 Review.
-
Pott's disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi: case report and review.Clin Infect Dis. 1994 Dec;19(6):1024-8. doi: 10.1093/clinids/19.6.1024. Clin Infect Dis. 1994. PMID: 7888528 Review.
References
-
- Sindel E. Empyema necessitatis. Bull Seaview Hosp 1940;6:1–49.
-
- Freeman AF, Ben-Ami T, Shulman ST. Streptococcus pneumoniae empyema necessitatis. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2004;23:177–9. 10.1097/01.inf.0000110625.41967.cc - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
