The central role of self-esteem in the quality of life of patients with mental disorders
- PMID: 35550549
- PMCID: PMC9098638
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11655-1
The central role of self-esteem in the quality of life of patients with mental disorders
Abstract
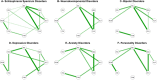
In psychiatry, recent years have seen a change of focus from a clinician- to a patient-centered perspective that emphasizes quality of life as a treatment target. As a complex construct, quality of life is composed of multiple dimensions that interact with one-another (e.g. physical and psychological well-being, relationships, autonomy, self-esteem). Here, we used data from the REHABase cohort, which includes N = 2180 patients from 15 psychosocial rehabilitation centers in France, to explore networks of quality-of-life dimensions among six psychiatric disorders: schizophrenia, neurodevelopmental, bipolar, depressive, anxiety, and personality disorders. Stronger connections (edges) involved the Self-Esteem dimension, such as Self-Esteem-Physical Well-Being, Self-Esteem-Autonomy, Self-Esteem-Psychological Well-Being, and Self-Esteem-Resilience. Self-esteem was also consistently retrieved as the most central node (the dimension with the most connections within each network). Between-group tests did not reveal any differences regarding network structure, overall connectivity, edge-weights, and nodes' centrality. Despite presenting with different symptom profiles, various psychiatric disorders may demonstrate similar inter-relationships among quality-of-life dimensions. In particular, self-esteem may have a crucial inter-connecting role in patients' quality of life. Our findings could support treatment programmes that specifically target self-esteem to improve patients' quality of life in a cost-effective way.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. Preamble to the Constitution of the World Health Organization as adopted by the International Health Conference, New York, 19–22 June, 1946; signed on 22 July 1946 by the representatives of 61 States (Official Records of the World Health Organization, no. 2, 100, 1948) and entered into force on 7 April 1948.
-
- Chaudhury S, et al. Quality of life in psychiatric disorders. Trends Biomed. Res. 2018;1:103. doi: 10.15761/JTBR.1000103. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

